Netgear WNDR3700 WNDR3700 User Manual - Page 62
Table 4-1., Wireless Router Status Fields, information, as described - model
 |
UPC - 606449061314
View all Netgear WNDR3700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 62 highlights
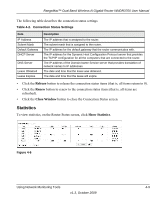
RangeMax™ Dual Band Wireless-N Gigabit Router WNDR3700 User Manual You can use the Show Statistics and Connection Status buttons to view additional status information, as described in "Connection Status" on page 4-8 and "Statistics" on page 4-9. The following table explains Router Status screen fields. Table 4-1. Wireless Router Status Fields Field Description Hardware Version The router model. Firmware Version The version of the router firmware. It changes if you upgrade the router. GUI Language Version The localized language of the GUI. Internet Port MAC Address The Media Access Control address. This is the unique physical address being used by the Internet (WAN) port of the router. IP Address The IP address being used by the Internet (WAN) port of the router. If no address is shown, or is 0.0.0.0, the router cannot connect to the Internet. DHCP • None. The router uses a fixed IP address on the WAN. • DHCP Client. The router obtains an IP address dynamically from the ISP. IP Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask being used by the Internet (WAN) port of the router. For an explanation of subnet masks and subnet addressing, click the link to the online document "TCP/IP Networking Basics" in Appendix B. Domain Name Server The Domain Name Server addresses being used by the router. A Domain Name Server translates human-language URLs such as www.netgear.com into IP addresses. Using Network Monitoring Tools 4-6 v1.3, October 2009