3Com 3CBLSF50 User Guide - Page 54
IGMP Snooping & Query, This switch uses IGMP Internet Group Management
 |
UPC - 662705529103
View all 3Com 3CBLSF50 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 54 highlights
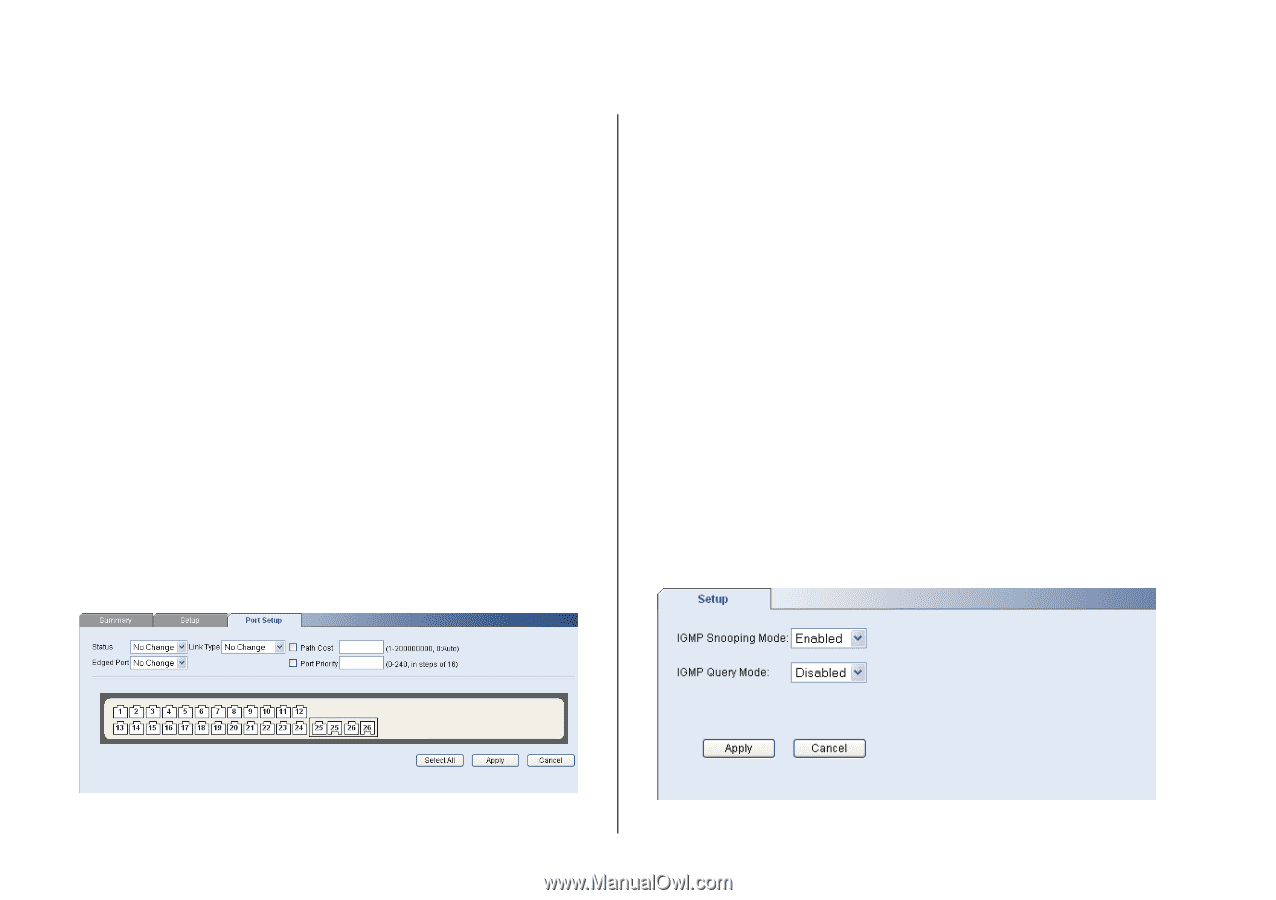
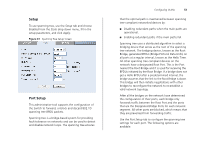
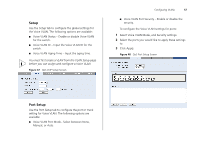
54 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH FROM THE WEB INTERFACE ■ Status - Enables and disables spanning tree for the port. ■ Edged Port - Enables and disables edged port for the port. ■ Link Type - Choose between Point-to-Point, Shared, or Auto for the link type. ■ Path Cost - The path cost is used to determine the best path between devices. The path cost method is used to determine the range of values that can be assigned to each interface. ■ Port Priority - Used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the STA root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest MAC address will then become the root device. If you modify any of these settings, click Apply to save your changes. Figure 42 Spanning Tree Port Setup Screen IGMP Snooping & Query This switch uses IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to query for any attached hosts that want to receive a specific multicast service. It identifies the ports containing hosts requesting to join the service and sends data out to those ports only. It then propagates the service request up to any neighboring multicast switch/router to ensure that it will continue to receive the multicast service. This procedure is called multicast filtering. The purpose of IP multicast filtering is to optimize a switched network's performance, so multicast packets will only be forwarded to those ports containing multicast group hosts or multicast routers/switches, instead of flooding traffic to all ports in the subnet (VLAN). Choose Enabled or Disabled from the IGMP Snooping Mode drop down menu. Figure 43 IGMP Snooping & Query Setup Screen