HP 635n HP Jetdirect Print Servers - How to Use 802.1X on HP Jetdirect Print S - Page 6
What is 802.1X?
 |
UPC - 882780301016
View all HP 635n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
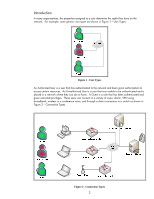
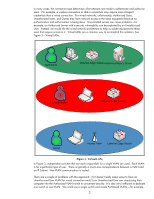
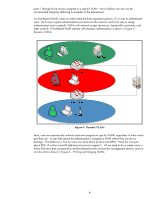
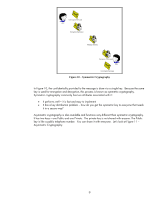
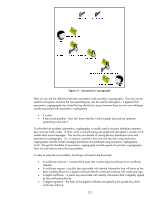
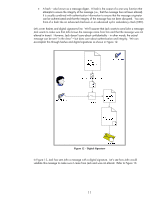
What is 802.1X? IEEE 802.1X Port Access Control is a generic framework that allows infrastructure devices to control an end-node's access to the network. From an Ethernet perspective, we can refer to Figure 6 - 802.1X Switch Port, and see the breakdown of the Ethernet switch. Ethernet Switch Switch Port 1 Switch Port 2 Switch Port 3 Switch Port N.... Local Intranet Switch Port Detail To Switch Bus LAN PORT 802.1X Figure 6 - 802.1X Switch Port The end-node device must authenticate itself to the network before the local switch will grant it access to the network. The end-node device has a valid link to the switch, but the only frames the switch will forward from the end-node to the network are 802.1X Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) frames. The technical terminology for the devices involved is shown in Figure 7 - 802.1X Terms. Figure 7 - 802.1X Terms In reality, the authenticator (switch) repackages 802.1X EAP frames from the Supplicant and sends them to an Authentication Server. Based upon the configuration in the Authentication Server and the information supplied by the Supplicant, the Supplicant is authenticated (or not). The result of this authentication determines whether the switch port is "opened up" to the network for the Supplicant to send/receive non-EAP frames for normal network operation. With HP ProCurve switches, the Authentication Server can return much more information, such as the VLAN the Supplicant should be assigned, bandwidth restrictions on the Supplicant, etc., and the switch dynamically configures itself to support those parameters. 6