HP 635n HP Jetdirect Print Servers - How to Use 802.1X on HP Jetdirect Print S - Page 62
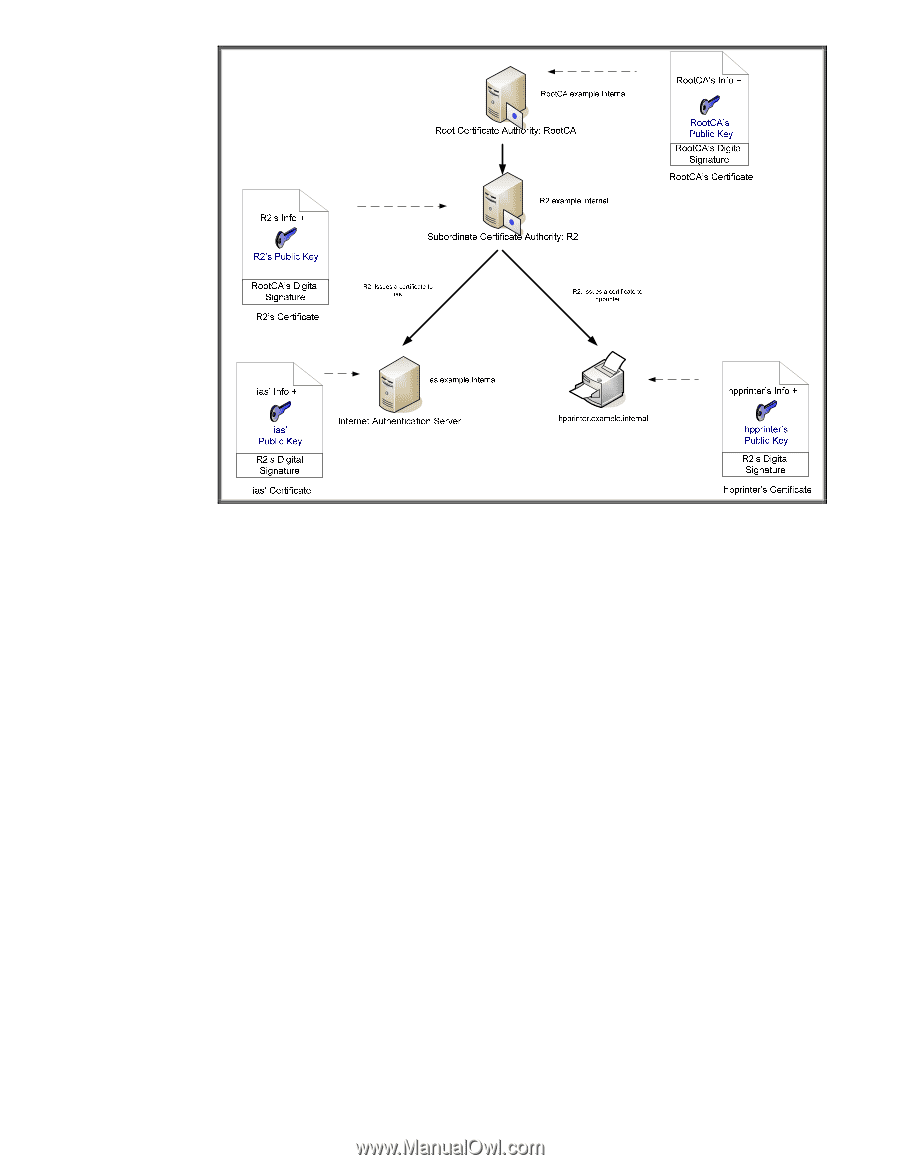
CA Hierarchy
 |
UPC - 882780301016
View all HP 635n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 62 highlights
Figure 22 - CA Hierarchy In this example, RootCA is the top level CA, which is also called the Root. What usually happens at customer sites is that the Root CA is created and it issues one or more certificates to Subordinate CAs, also known as Intermediate CAs, and they do the dirty work of issuing certificates to various entities in the customer's network. The Root CA is then shutdown and locked up in a secure room with this information backed up in several places. The Root CA establishes the trust of the whole environment and is very well protected. We can see that RootCA issues a certificate to R2, which grants R2 the capability to issue certificates to other entities. R2's certificate is signed by the Root CA. R2 then can issue certificates to other devices, such as IAS. If we take a look at IAS' certificate, the issuing "chain" or path looks like Figure 23: 62