HP 635n HP Jetdirect Print Servers - How to Use 802.1X on HP Jetdirect Print S - Page 82
Client Authentication Problem
 |
UPC - 882780301016
View all HP 635n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 82 highlights
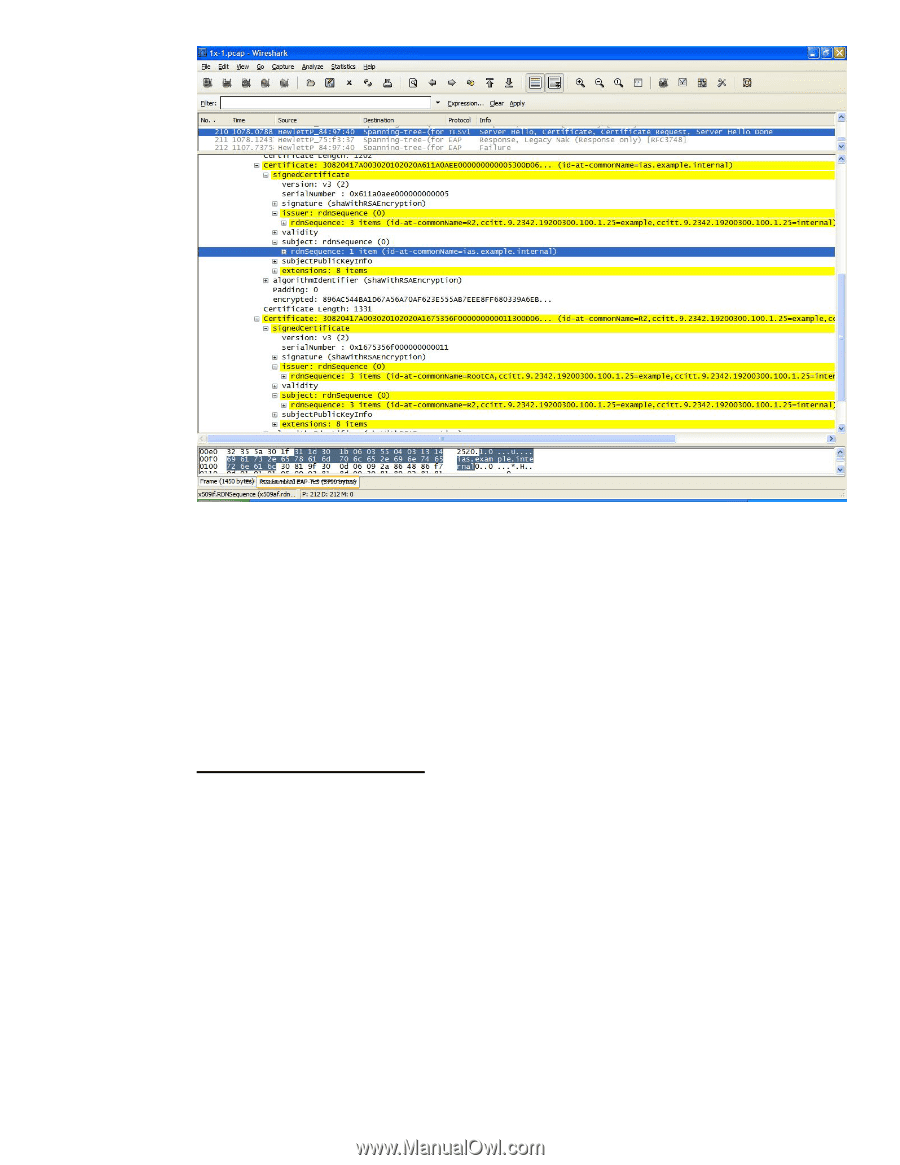
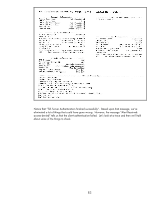
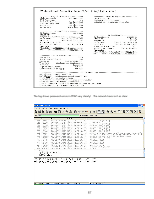
By looking at each certificate's "Issuer" and "Subject" fields, we can determine what is Jetdirect is seeing. Since "ias.example.internal" is the Authentication Server certificate and its common name is shown as "ias.example.internal", we know that the Server ID needs to be configured correctly to handle that value. The "Issuer" of this certificate is R2.example.internal. Jetdirect needs to have the public key certificate of R2 in order to verify the signature on ias.example.internal. The Authentication Server also sends back the R2.example.internal certificate. This certificate is issued by RootCA. Jetdirect also needs the RootCA public key certificate. This certificate, RootCA must be configured on Jetdirect as the CA Certificate in order for the certificate chain to be verified. These two situations are the most common type of issues that affect 802.1X configurations. Client Authentication Problem Assuming that everything went ok with Server Authentication, then client authentication is the next area where there could be problems. For EAP-TLS, the client sends a certificate to authenticate while in PEAP, a username/password is sent using a different protocol to authenticate the client. In both cases, the certificate or the username/password must be mapped to an account that is granted access. Let's look at an EAP-TLS client authentication problem. 82