HP ProLiant DL360e HP Intelligent Provisioning User Guide - Page 26
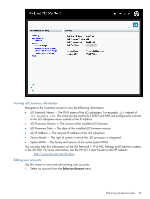
Displays the iLO MAC Address., iLO Gateway IP Address
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL360e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
1. Configure the following options: • Enable DHCP - Enables iLO to obtain its IP address (and many other settings) from a DHCP server. If DHCP is disabled, enter the following: ◦ iLO IP Address - The iLO IP address. If DHCP is used, the iLO IP address is supplied automatically. ◦ iLO Subnet Mask - The subnet mask of the iLO IP network. If DHCP is used, the Subnet Mask is supplied automatically. ◦ iLO Gateway IP Address - The iLO gateway address. If DHCP is used, the gateway address is supplied automatically. • iLO DNS Name - The DNS name of the iLO subsystem, for example, ilo instead of ilo.example.com. This name can be used only if DHCP and DNS are configured to connect to the iLO DNS name instead of the IP address. Observe the following iLO DNS name limitations: ◦ Name service limitations - The subsystem name is used as part of the DNS name and WINS name. The DNS and WINS limitations differ: - DNS allows alphanumeric and hyphen. WINS allows alphanumeric, hyphen, and underscore. - WINS subsystem names are truncated at 15 characters, DNS names are not. If you require underscores, they can be entered in RBSU or with the iLO scripting utility. NOTE: Name service limitations also apply to the domain name. ◦ To avoid name space issues: - Do not use the underscore character. - Limit subsystem names to 15 characters. - Verify that you can PING iLO by IP address and by DNS/WINS name. - Verify NSLOOKUP correctly resolves the iLO network address and no namespace conflicts exist. - Verify DNS and WINS both correctly resolve the name (if you are using both). - Flush the DNS name if you make any namespace changes. • iLO MAC Address - Displays the iLO MAC Address. • Network Interface Adapter - Enables or disables the primary iLO network interface. If you set this to disabled, you must use the iLO RBSU or another host-based scripting utility to re-enable the network interface. • Transceiver Speed Autoselect - Enables iLO to negotiate the highest supported link speed and duplex when connected to the network. • Transceiver Speed - Enables you to specify a link speed when Transceiver Speed Autoselect is disabled. Select 10 Mbits/s, 100 Mbits/s, or 1 Gbits/s. • Transceiver Duplex Setting - Enables you to select half or full duplex when Transceiver Speed Autoselect is disabled. • Enable Shared Network Port - Enables networking using the Embedded host Ethernet port. The Shared Network Port has a different Ethernet MAC address than the dedicated Ethernet port. This option is available only if your server supports the required hardware. 26 Using Intelligent Provisioning