HP ProLiant xw2x220c Remote Graphics Software 5.3.0 User Guide - Page 119
Receiver network timeouts, Receiver Control Panel
 |
View all HP ProLiant xw2x220c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
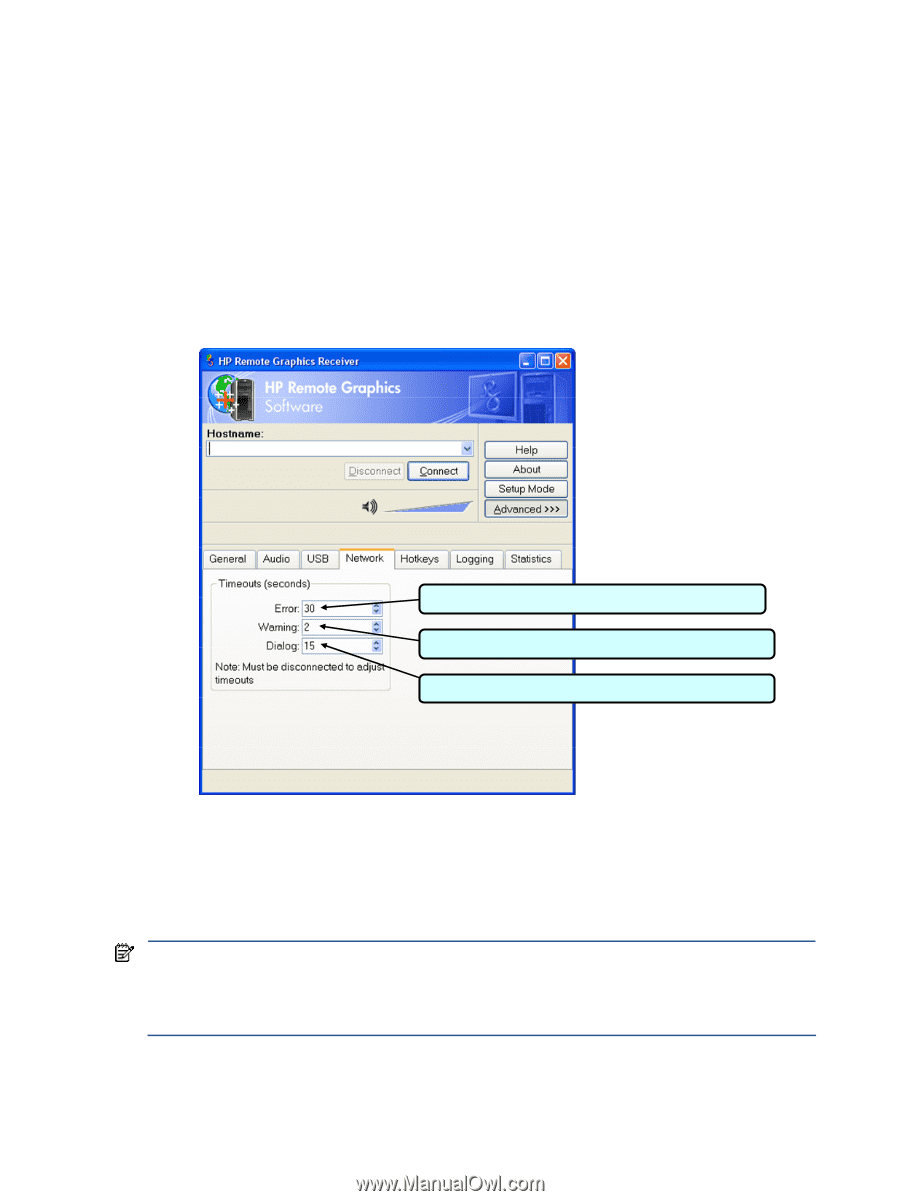
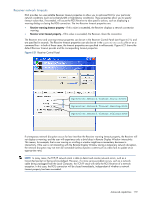
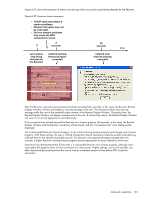
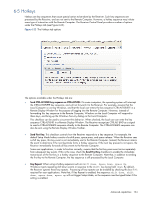
Receiver network timeouts RGS provides two user-settable Receiver timeout properties to allow you to optimize RGS for your particular network conditions (such as low-bandwidth or high-latency conditions). These properties allow you to specify timeout values that, if exceeded, will cause the RGS Receiver to take specific actions, such as displaying a warning dialog or closing the RGS connection. The two Receiver timeout properties are: • Receiver warning timeout property-If this value is exceeded, the Receiver displays a network connection warning. • Receiver error timeout property-If this value is exceeded, the Receiver closes the connection. The Receiver error and warning timeout properties can be set in the Receiver Control Panel (see Figure 6-21), and are specified in seconds. The Receiver timeout properties can also be set in the rgreceiverconfig file or on a command line-in both of these cases, the timeout properties are specified in milliseconds. Figure 6-21 shows the default Receiver timeout periods and the corresponding timeout properties. Figure 6-21 Receiver Control Panel Rgreceiver.Network.Timeout.Error=30000 Rgreceiver.Network.Timeout.Warning=2000 Rgreceiver.Network.Timeout.Dialog=15000 If a temporary network disruption occurs for less time than the Receiver warning timeout property, the Receiver will not display a warning, and the user will experience only a brief drop in Remote Display Window interactivity. This means, for example, that a user moving or scrolling a window might see a momentary decrease in interactivity. If the user is not interacting with the Remote Display Window during a temporary network disruption, the network disruption may not even be noticeable (unless dynamic content such as video fails to update at an appropriate rate). NOTE: In many cases, the TCP/IP network stack is able to detect and resolve network errors, such as a transmitted packet not being acknowledged. However, if a more serious problem occurs, such as a network cable being unplugged from the Local Computer, the TCP/IP stack will notify the RGS Receiver of a network exception. In this case, the RGS connection will be closed immediately, independent of whether a network timeout property has been exceeded. Advanced capabilities 119