HP ProLiant xw2x220c Remote Graphics Software 5.3.0 User Guide - Page 40
Support of sound recording devices on Microsoft Windows XP Professional
 |
View all HP ProLiant xw2x220c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
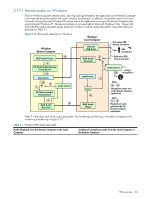
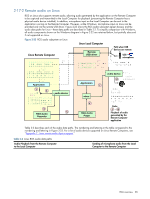
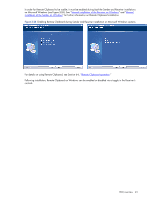
2-17-3 Support of sound recording devices on Microsoft Windows XP Professional NOTE: The Windows Sounds and Audio Devices Properties dialog allows the user to select the "sound recording device". For simplicity, "microphone" is used below instead of "sound recording device". Remote microphone is not supported on Microsoft Windows Vista. Prior to RGS 5.2.0, a Receiver-attached USB microphone couldn't be remotely connected to the Sender in the same manner as other remote USB devices (see Section 2-16, "Remote USB overview"). Audio from a Receiverattached USB microphone would need to be first processed by the Windows USB audio driver on the Receiver. The audio would then be sent to the RGS Audio Recorder (see Figure 2-22) for capture and transmission to the Sender. In order for a USB microphone to be used in this manner, USB devices are Local must be selected in the Remote USB Configuration dialog during installation. This ensures the USB microphone is a local device, allowing its audio to be captured by the RGS Audio Recorder. This capability allows use of any USB microphone supported by Windows. At RGS 5.2.0, the Remote USB driver (on the Local Computer) has been enhanced to support the USB isochronous data type, which is commonly used for streaming data such as that generated by audio and video devices. This enables certain isochronous USB microphones to be accessed directly by the Remote Computer in the same manner as other USB devices. See Appendix B for a list of supported USB microphones (listed under Sound recording devices). To remotely attach USB microphones to the Remote Computer, either of these Remote USB Configuration settings can be selected: • USB devices are Remote • USB devices are Local/Remote If USB devices are Remote is selected, a USB microphone can be accessed anytime by the Remote Computer. If USB devices are Local/Remote is selected, how the USB microphone can be accessed by the Remote Computer depends on when the microphone is connected to the Local Computer relative to establishment of the RGS connection. If the microphone is connected to the Local Computer prior to establishment of the RGS connection, the microphone will be a local device only, and will be accessible by the Remote Computer only via the Receiver RGS Audio Recorder. If the microphone is connected to the Local Computer after RGS connection establishment, the microphone will be a remote device only, and can be accessed directly by the Remote Computer. Figure 2-19 shows these two cases. HP recommends using the audio access method introduced at RGS 5.2.0, whereby the Remote Computer can directly access the USB microphone, for the following reasons: • The pre-RGS 5.2.0 audio access method continuously records and transmits audio independent of whether the application on the Remote Computer is requesting audio input. This can consume network bandwidth, especially when the level of background noise at the microphone is above the audio threshold used to detect valid audio. • The RGS 5.2.0 audio access method allows audio parameters to be set by audio controls on the Remote Computer alone. The pre-RGS 5.2.0 audio access method requires setting audio parameters on both the Remote Computer and Local Computer. RGS overview 40