IBM 2498-B40 User Guide - Page 53
Interpreting POST results, SAN48B-5 maintenance, Diagnostic testing, Fabric OS Administrator's Guide
 |
View all IBM 2498-B40 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
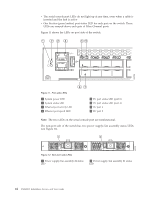
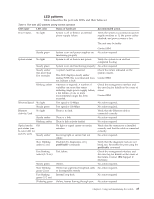
Interpreting POST results POST is a system check that is performed each time the switch is powered on, rebooted, or reset. During POST, the LEDs flash either amber or green. Any errors that occur during POST are listed in the error log. Complete the following steps to determine whether POST completed successfully and whether any errors were detected. 1. Verify that the switch LEDs indicate that all components are healthy. See Table 4 on page 25 and Table 5 on page 26 for descriptions and interpretations of LED patterns. If one or more LEDs do not display a healthy state, verify that the LEDs on the switch are not set to "beacon" by entering the switchShow command to detect if beaconing is active. 2. Verify that the switch prompt displays on the terminal of a computer workstation connected to the switch. If there is no switch prompt when POST completes, press Enter. If the switch prompt still does not display, try opening a Telnet session or accessing the switch through another management tool. If this is not successful, the switch did not successfully complete POST. Contact IBM. 3. Review the switch system log for errors. Any errors detected during POST are written to the system log, accessible through the errShow command. For information about all referenced commands, and on accessing the error log, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator's Guide. For information about error messages, refer to the Fabric OS Message Reference Manual. SAN48B-5 maintenance The SAN48B-5 is designed for high availability and low failure; it does not require any regular physical maintenance. It includes diagnostic tests and field-replaceable units, described in the following sections. Diagnostic testing In addition to POST, the Fabric OS includes diagnostic tests to troubleshoot the hardware and firmware. This includes tests of internal connections and circuitry, fixed media, and the transceivers and cables. The tests are implemented by command, either through a Telnet session or through a terminal set up for a serial connection to the switch. Some tests require the ports to be connected by external cables, to allow diagnostics to verify the serializer/deserializer interface, transceiver, and cable. Some tests require loopback plugs. Diagnostic tests are run at link speeds of 2, 4, 8, 10 or 16 Gbps (FC) depending on the speed of the link being tested and the type of port. Note: Diagnostic tests might temporarily lock the transmit and receive speed of the links during diagnostic testing. For information about specific diagnostic tests, see the Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide. Chapter 3. Using and maintaining the switch 27