TRENDnet TEW-751DR User's Guide - Page 38
Port Forwarding, Application Name, <<, Computer Name
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-751DR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
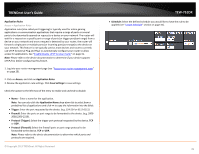
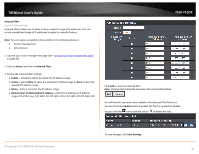
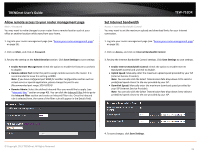
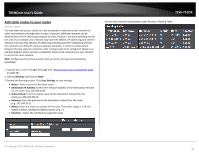
TRENDnet User's Guide Port Forwarding Access > Port Forwarding Port Forwarding allows you to define a range of multiple public ports (used or required by a specific application or game) and forward them to a single IP address (a computer or device) on your network on a specific port. Using this feature is more secure compared to using DMZ (see "DMZ" on page 36) in which DMZ forwards all ports instead of only specific ports used by an application. Since most ISPs constantly change your home IP address, to be able to access the Virtual Server port(s) from the Internet it is recommended to setup Dynamic DNS service (see "Identify your network over the Internet" section on page 33). 1. Log into your router management page (see "Access your router management page" on page 25). 2. Click on Access, and click on Port Forwarding. 3. Review the port forwarding settings. Click Save Settings to save settings. TEW-751DR Check the option to the left most of the entry to enable and uncheck to disable. • Name - Enter a name for the virtual server. Note: You can also click the Application Name drop-down list to select from a predefined list of applications and click