ZyXEL P-336M User Guide - Page 33
Wireless LAN Overview, Basic Wireless LAN Setup
 |
View all ZyXEL P-336M manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
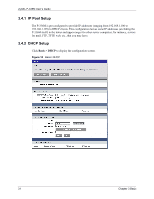
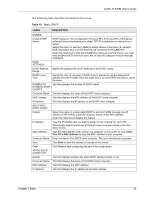
ZyXEL P-336M User's Guide 3.5 Wireless LAN Overview This section introduces the wireless LAN features. 3.5.1 SSID The SSID (Service Set Identity) is a unique name shared among all wireless devices in a wireless network. Wireless devices must have the same SSID to communicate with each other. 3.5.2 Channel A radio frequency used by a wireless device is called a channel. 3.5.3 Transmission Rate (Tx Rate) The P-336M provides various transmission (data) rate options for you to select. In most networking scenarios, the factory default Best (Automatic) setting proves the most efficient. This setting allows your P-336M to operate at the maximum transmission (data) rate. When the communication quality drops below a certain level, the P-336M automatically switches to a lower transmission (data) rate. Transmission at lower data speeds is usually more reliable. However, when the communication quality improves again, the P-336M gradually increases the transmission (data) rate again until it reaches the highest available transmission rate. You can select any of the above options. If you wish to balance speed versus reliability, select 54 Mbps in a networking environment where you are certain that all wireless devices can communicate at the highest transmission (data) rate. 1 Mbps or 2 Mbps are used often in networking environments where the range of the wireless connection is more important than speed. 3.5.3.1 SuperGTM The SuperG technology works with IEEE 802.11 a/b/g products. It doubles IEEE 802.11g performance by bonding two 54Mbps channels and allowing larger frames to be sent. IEEE 802.11g wireless LAN devices using Super G can transmit at up to 108 Mbps. 3.6 Basic Wireless LAN Setup Click Basic > Wireless to display the configuration screen. 33 Chapter 3 Basic