ZyXEL SBG3300-N Series User Guide - Page 108
SBG3300-N Series User's Guide
 |
View all ZyXEL SBG3300-N Series manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 108 highlights
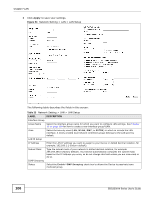
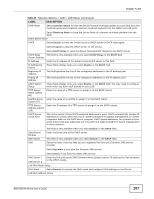
Chapter 7 LAN Table 33 Network Setting > LAN > LAN Setup (continued) LABEL DESCRIPTION Delegate prefix Select this option to automatically obtain an IPv6 network prefix from the service provider from WAN or an uplink router. Static Select this option to configure a fixed IPv6 address for the Device's LAN IPv6 address. Note: This fixed address is for local hosts to access the Web Configurator only as the global LAN IPv6 address might be changed by your ISP any time. This address is not the routing gateway's address for LAN IPv6 hosts. ULA PseudoRandom Global ID A unique local address (ULA) is a unique IPv6 address for use in private networks but not routable in the global IPv6 Internet. Select this to have the Device automatically generate a globally unique address for the LAN IPv6 address. The address format is like fdxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx::/64. ULA IPv6 Address Setup IPv6 Address If you select static IPv6 address, enter the IPv6 address prefix that the Device uses for the LAN IPv6 address. Prefix Length If you select static IPv6 address, enter the IPv6 prefix length that the Device uses to generate the LAN IPv6 address. MLD Snooping MLD Mode An IPv6 prefix length specifies how many most significant bits (starting from the left) in the address compose the network address. This field displays the bit number of the IPv6 subnet mask. Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) allows an IPv6 switch or router to discover the presence of MLD hosts who wish to receive multicast packets and the IP addresses of multicast groups the hosts want to join on its network. Select Enable MLD Snooping to activate MLD snooping on the Device. This allows the Device to check MLD packets passing through it and learn the multicast group membership. It helps reduce multicast traffic. Select Standard Mode to have the Device forward IPv6 multicast packets to a port that joins the IPv6 multicast group and broadcast unknown IPv6 multicast packets from the WAN to all LAN ports. Select Blocking Mode to have the Device block all unknown IPv6 multicast packets from the WAN. LAN IPv6 Address Assign Setup Select how you want to obtain an IPv6 address: • stateless + DNS send by RADVD: The Device uses IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration. RADVD (Router Advertisement Daemon) is enabled to have the Device send IPv6 prefix information in router advertisements periodically and in response to router solicitations. DHCPv6 server is disabled. (See page 104 for more information on RADVD.) • stateless + DNS send by DHCPv6: The Device uses IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration. The DNS is provided by a DHCPv6 server. • stateful + DHCPv6 server: The Device uses IPv6 stateful autoconfiguration. The DHCPv6 server is enabled to have the Device act as a DHCPv6 server and pass IPv6 addresses, DNS server and domain name information to DHCPv6 clients. • stateful + DHCPv6 relay: The Device uses IPv6 stateful autoconfiguration. DHCPv6 Relay is enabled to have the Device relay client DHCPv6 requests. DHCPv6 Configuration DHCPv6 State This shows the status of the DHCPv6. IPv6 DNS Values IPv6 DNS Server 1-3 Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns IPv6 DNS server information. Select User-Defined if you have the IPv6 address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server IPv6 addresses the Device passes to the DHCP clients. Select None if you do not want to configure IPv6 DNS servers. IPv6 Address Values IPv6 Start Address If DHCPv6 is enabled, specify the first IPv6 address in the pool of addresses that can be assigned to DHCPv6 clients. 108 SBG3300-N Series User's Guide