Dell XPS 600 Renegade Owner's Manual - Page 21
About Serial ATA Drives, About Your RAID Configuration, RAID Level 0 Configuration - gaming computer
 |
View all Dell XPS 600 Renegade manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
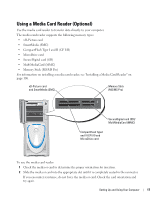
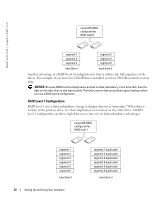
About Serial ATA Drives Your computer supports up to three serial ATA hard drives. Serial ATA drives provide the following benefits by transferring data using serial technology and flexible cables that are thinner and longer than IDE cables: • Improved cable routing facilitates more efficient airflow inside the chassis. • Compact cable connectors save space on the system board and on the hard drive. Combined with the improved cable routing, this allows a more efficient utilization of space inside the chassis. See "Hard Drive" on page 97 for information on serial ATA drive connections. About Your RAID Configuration NOTICE: If you might ever decide to migrate to a RAID array, before loading the operating system onto a hard drive, set up that drive as a single drive RAID 0 array. See "Creating an Array using the Nvidia MediaShield ROM Utility" on page 23 for instructions. This section provides an overview of the RAID configuration that you might have selected when you purchased your computer. Dell offers either a RAID level 0 configuration or a RAID level 1 configuration on your Dell™ XPS computer. A RAID level 0 configuration is recommended for high-performance gaming, and a RAID level 1 configuration is recommended for the data integrity requirements of digital photography and audio. NOTE: RAID levels do not represent a hierarchy. A RAID level 1 configuration is not inherently better or worse than a RAID level 0 configuration. The drives in an array should be the same size in order to ensure that the larger drive does not contain unallocated (and therefore unusable) space. RAID Level 0 Configuration A RAID level 0 configuration uses a storage technique known as "data striping" to provide a high data access rate. Data striping is a method of writing consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical drives to create a large virtual drive. Data striping allows one of the drives to read data while the other drive is searching for and reading the next block. Setting Up and Using Your Computer 21