Netgear WGX102 WGX102v2 Reference Manual - Page 130
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
 |
View all Netgear WGX102 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
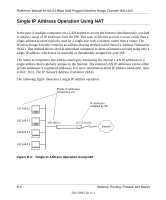
Reference Manual for the 54 Mbps Wall-Plugged Wireless Range Extender WGX102 Single IP Address Operation Using NAT In the past, if multiple computers on a LAN needed to access the Internet simultaneously, you had to obtain a range of IP addresses from the ISP. This type of Internet account is more costly than a single-address account typically used by a single user with a modem, rather than a router. The Wireless Range Extender employs an address-sharing method called Network Address Translation (NAT). This method allows several networked computers to share an Internet account using only a single IP address, which may be statically or dynamically assigned by your ISP. The router accomplishes this address sharing by translating the internal LAN IP addresses to a single address that is globally unique on the Internet. The internal LAN IP addresses can be either private addresses or registered addresses. For more information about IP address translation, refer to RFC 1631, The IP Network Address Translator (NAT). The following figure illustrates a single IP address operation. Private IP addresses assigned by user 192.168.0.2 IP addresses assigned by ISP 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.1 172.21.15.105 Internet 192.168.0.5 Figure B-3: Single IP Address Operation Using NAT 7786EA B-8 Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics 202-10042-02 v1.1