Netgear WGX102 WGX102v2 Reference Manual - Page 132
Domain Name Server, IP Configuration by DHCP, Internet Security and Firewalls
 |
View all Netgear WGX102 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 132 highlights
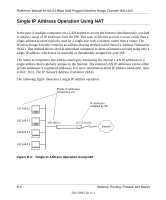
Reference Manual for the 54 Mbps Wall-Plugged Wireless Range Extender WGX102 Domain Name Server Many of the resources on the Internet can be addressed by simple descriptive names such as http://www.NETGEAR.com. This addressing is very helpful at the application level, but the descriptive name must be translated to an IP address in order for a user to actually contact the resource. Just as a telephone directory maps names to phone numbers, or as an ARP table maps IP addresses to MAC addresses, a domain name system (DNS) server maps descriptive names of network resources to IP addresses. When a computer accesses a resource by its descriptive name, it first contacts a DNS server to obtain the IP address of the resource. The computer sends the desired message using the IP address. Many large organizations, such as ISPs, maintain their own DNS servers and allow their customers to use the servers to look up addresses. IP Configuration by DHCP When an IP-based local area network is installed, each computer must be configured with an IP address. If the computers need to access the Internet, they should also be configured with a gateway address and one or more DNS server addresses. As an alternative to manual configuration, there is a method by which each computer on the network can automatically obtain this configuration information. A device on the network may act as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. The DHCP server stores a list or pool of IP addresses, along with other information (such as gateway and DNS addresses) that it may assign to the other devices on the network. The Wireless Range Extender has the capacity to act as a DHCP server. The Wireless Range Extender also functions as a DHCP client when connecting to the ISP. The router can automatically obtain an IP address, subnet mask, DNS server addresses, and a gateway address if the ISP provides this information by DHCP. Internet Security and Firewalls When your LAN connects to the Internet through a router, an opportunity is created for outsiders to access or disrupt your network. A NAT router provides some protection because by the very nature of the process, the network behind the router is shielded from access by outsiders on the Internet. However, there are methods by which a determined hacker can possibly obtain information about your network or at the least can disrupt your Internet access. A greater degree of protection is provided by a firewall router. B-10 Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics 202-10042-02 v1.1