HP Mellanox SX1018 Mellanox MLNX-OS® User Manualfor SX1018HP Ethernet - Page 8
Glossary
 |
View all HP Mellanox SX1018 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
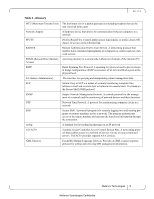
Glossary Table 3 - Glossary AAA ARP CLI DCB DCBX DHCP DNS ETS FTP/TFTP/sFTP Gateway HA (High Availability) Host LACP LDAP MAC Rev 1.6.9 Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting. Authentication - verifies user credentials (username and password). Authorization - grants or refuses privileges to a user/client for accessing specific services. Accounting - tracks network resources consumption by users. Address Resolution Protocol. A protocol that translates IP addresses into MAC addresses for communication over a local area network (LAN). Command Line Interface. A user interface in which you type commands at the prompt Data Center Bridging DCBX protocol is an extension of the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP). DCBX end points exchange request and acknowledgment messages. For flexibility, parameters are coded in a type-length-value (TLV) format. The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an automatic configuration protocol used on IP networks. Domain Name System. A hierarchical naming system for devices in a computer network ETS provides a common management framework for assignment of bandwidth to traffic classes. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. A network node that interfaces with another network using a different network protocol A system design protocol that provides redundancy of system components, thus enables overcoming single or multiple failures in minimal downtime A computer platform executing an Operating System which may control one or more network adapters Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a method to control the bundling of several physical ports together to form a single logical channel. LACP allows a network device to negotiate an automatic bundling of links by sending LACP packets to the peer (directly connected device that also implements LACP). The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an application protocol for reading and editing directories over an IP network. A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies including Ethernet. Mellanox Technologies 8 Mellanox Technologies Confidential