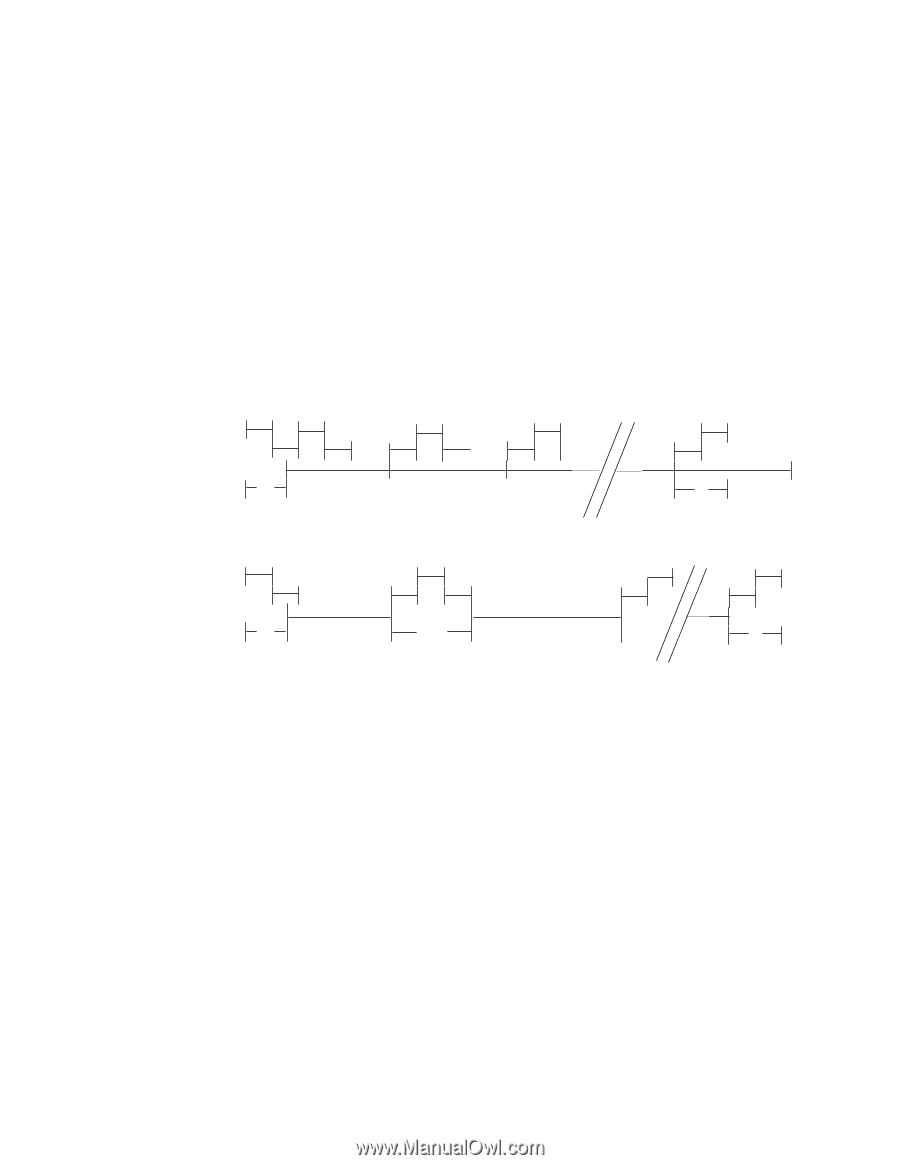Hitachi HDS728080PLAT20 Specifications - Page 102
Seek overlap
 |
UPC - 829686000094
View all Hitachi HDS728080PLAT20 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 102 highlights
10.9 Seek overlap HDS7280x0PLATy0 provides an accurate method for measuring seek time. The seek command is usually used to measure the device seek time by accumulating the execution time for a number of seek commands. With typical implementation of seek command this measurement must include the device and host command overhead. To eliminate this overhead the drive overlaps the seek command as described below. The first seek command is completed before the actual seek operation is ended. Then the device can receive the next seek command from the host; however, the actual seek operation for the next seek command starts immediately after the actual seek operation for the first seek command is completed. In other words, the execution of two seek commands overlaps excluding the time required for the actual seek operation. With this overlap the total elapsed time for a number of seek commands results in the total accumulated time for actual seek operation plus one pre- and post-overhead. When the number of seeks is large, only one overhead may be ignored. Table 69: Seek overlap ( 1) Wi t h over l ap Host pr ocess Devi ce pr ocess Seek oper at i on Over head A B Tot al t i me = ( n- 1) * ( Seek oper at i on) + A + B ( 2) Wi t hout over l ap Host pr ocess Devi ce pr ocess Seek oper at i on Over head A B+A B Tot al t i me = n * ( Seek oper at i on + A + B) Deskstar 7K80 Hard Disk Drive Specification 98