Hitachi HDS728080PLAT20 Specifications - Page 32
Throughput
 |
UPC - 829686000094
View all Hitachi HDS728080PLAT20 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
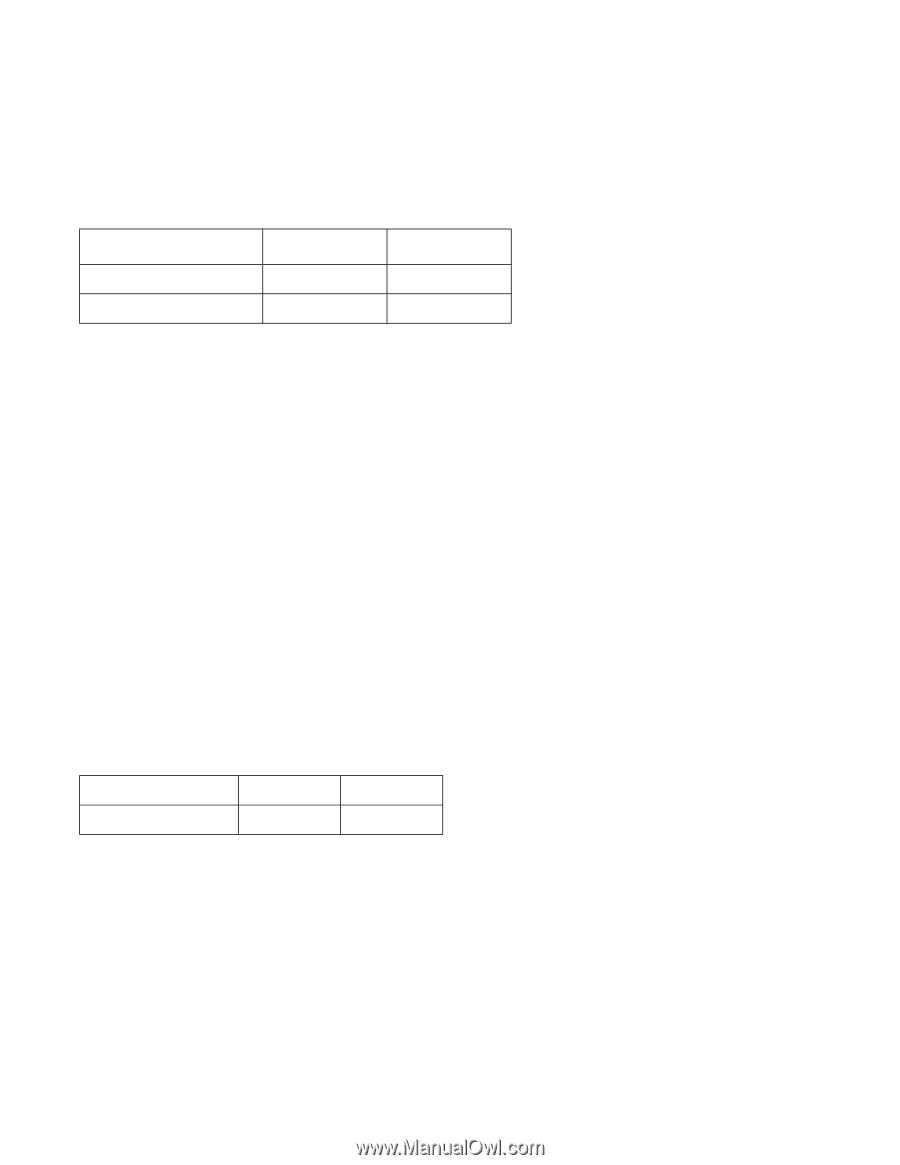
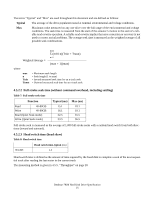
4.5.5 Throughput 4.5.5.1 Simple sequential access The following table illustrates simple sequential access for the enclosure. Table 13: Simple Sequential Access performance Operation Sequential Read (Zone 0) Sequential Read (Zone 29) Typical (sec) 0.3 0.61 Max (sec) 0.32 0.63 The above table gives the time required to read a total of 8000h consecutive blocks (16,777,216 bytes) accessed by 128 read commands. Typical and Max values are given by 105% and 110% of T respectively throughout following performance description. where T = A + B + C + 16,777,216/D + 512/E (READ) T = Calculated time (sec) A = Command process time (Command overhead) (sec) B = Average seek time (sec) C = Average latency (sec) D = Sustained disk-buffer transfer rate (byte/sec) E = Buffer-host transfer rate (byte/sec) Note: It is assumed that a host system responds instantaneously and host data transfer is faster than sustained data rate. 4.5.5.2 Random access The following table illustrates simple sequential access for enclosure. Table 14: Random Access Performance Operation Typical (sec) Max (sec) Random Read 55.9 58.6 The above table gives the time required to execute a total of 1000h read commands which access a single random LBA. Typical and Max values are given by 105% and 110% of T respectively throughout following performance description. T = 4096(A + B + C+ 512/D + 512/E) (READ) where T = Calculated time (sec) A = Command process time (Command overhead) (sec) B = Average seek time (sec) C = Latency Deskstar 7K80 Hard Disk Drive Specification 28