IBM DTCA-24090 Hard Drive Specifications - Page 78
Diagnostic and Reset considerations
 |
View all IBM DTCA-24090 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 78 highlights
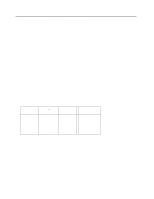
10.2 Diagnostic and Reset considerations For each Reset and Execute Device Diagnostic, the diagnostic is done as follows: Power On Reset, Hard Reset DASP- is read by Device 0 to determine if Device 1 is present. If Device 1 is present Device 0 shall read PDIAG- to determine when it is valid to clear the BSY bit and whether Device 1 has powered on or reset without error, otherwise Device 0 clears the BSY bit whenever it is ready to accept commands. Device 0 may assert DASPto indicate device activity. If Device 1 is not present, Device 0 does not Assert DASP- at POR. Soft Reset If Device 1 is present Device 0 shall read PDIAG- to determine when it is valid to clear the BSY bit and whether Device 1 has reset without any errors, otherwise Device 0 shall simply reset and clear the BSY bit. DASP- is asserted by Device 0 (and Device 1 if it is present) in order to indicate device active. Execute Device Diagnostic If Device 1 is present, Device 0 shall read PDIAG- to determine when it is valid to clear the BSY bit and if Device 1 passed or failed the EXECUTE DEVICE DIAGNOSTIC command, otherwise Device 0 shall simply execute its diagnostics and then clear the BSY bit. DASP- is asserted by Device 0 (and Device 1 if it is present) in order to indicate the device is active. In all the above cases: Power on, RESET-, Soft reset, and the EXECUTE DEVICE DIAGNOSTIC command the Device 0 Error register is shown in Figure 47. Device 1 Present? PDIAG Asserted? Device 0 Passed Error Register Yes Yes Yes 01h Yes Yes No 0xh Yes No Yes 81h Yes No No 8xh No (not read) Yes 01h No (not read) No 0xh Where x indicates the appropriate Diagnostic Code for the Power on, RESET-, Soft reset, or Device Diagnostic error. Figure 47. Reset error register values 70 OEM Specifications of DTCA-2xxxx 2.5 inch H D D