Intel 2011B Configuration Guide - Page 18
Link Required Operation for Maintaining Ethernet Link
 |
UPC - 735858150187
View all Intel 2011B manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
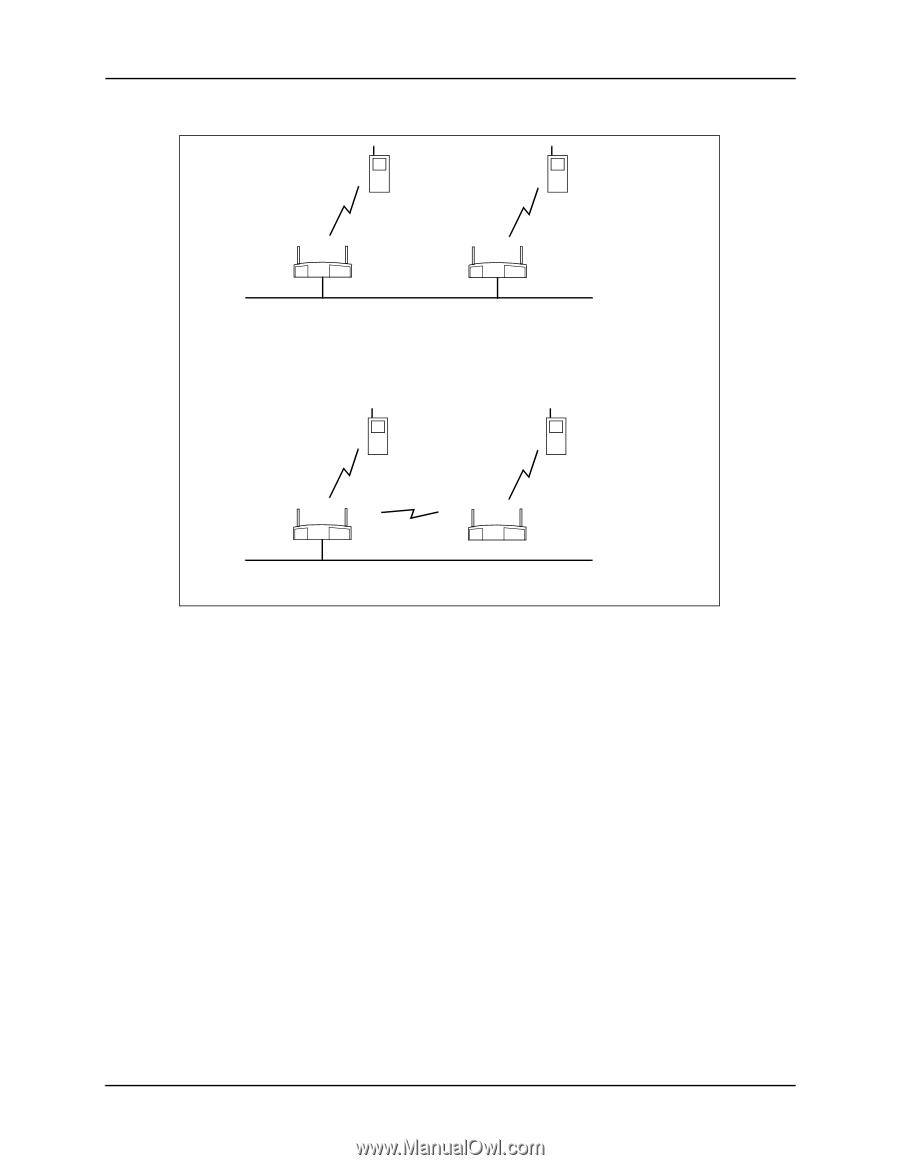
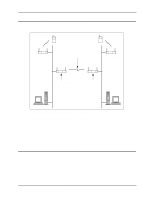
Chapter 4. Using the Link Required Option A B Ethernet Settings on Both Access Points: WLAP Mode = Link Required. WLAP Priority = 8000. WLAP Manual BSS ID = 0. Ethernet Timeout = 0. A B Ethernet If an access point loses its Ethernet connection, it resets and makes a wireless link to the Ethernet through the other access point. Figure 4-2: Link Required Operation for Maintaining Ethernet Link By viewing the WLAP RF Statistics screen, you can determine whether or not a wireless link exists between access points. In the example network in Figure 4-2, no wireless link exists between the access points as long as they are both connected to the Ethernet. For this condition, the WLAP RF Statistics screen (Figure 4-3) shows the Current State as Functional, the Itf State as DIS (disabled), and the WLAP Itf MAC Addr as zero. If one of the access points in the network in Figure 4-2 loses its Ethernet connection, it resets and initiates a wireless connection with the other access point. When the process of making the wireless link is completed, the WLAP RF Statistics screen (Figure 4-4) shows the Itf State as FWD (forward) and the WLAP Itf MAC Addr as the MAC address of the other access point. 12 Configuring Access Point Bridging and Repeating (WLAP Mode)