Intel 2011B Configuration Guide - Page 7
Introduction, Basic Settings for Access Points - firmware
 |
UPC - 735858150187
View all Intel 2011B manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
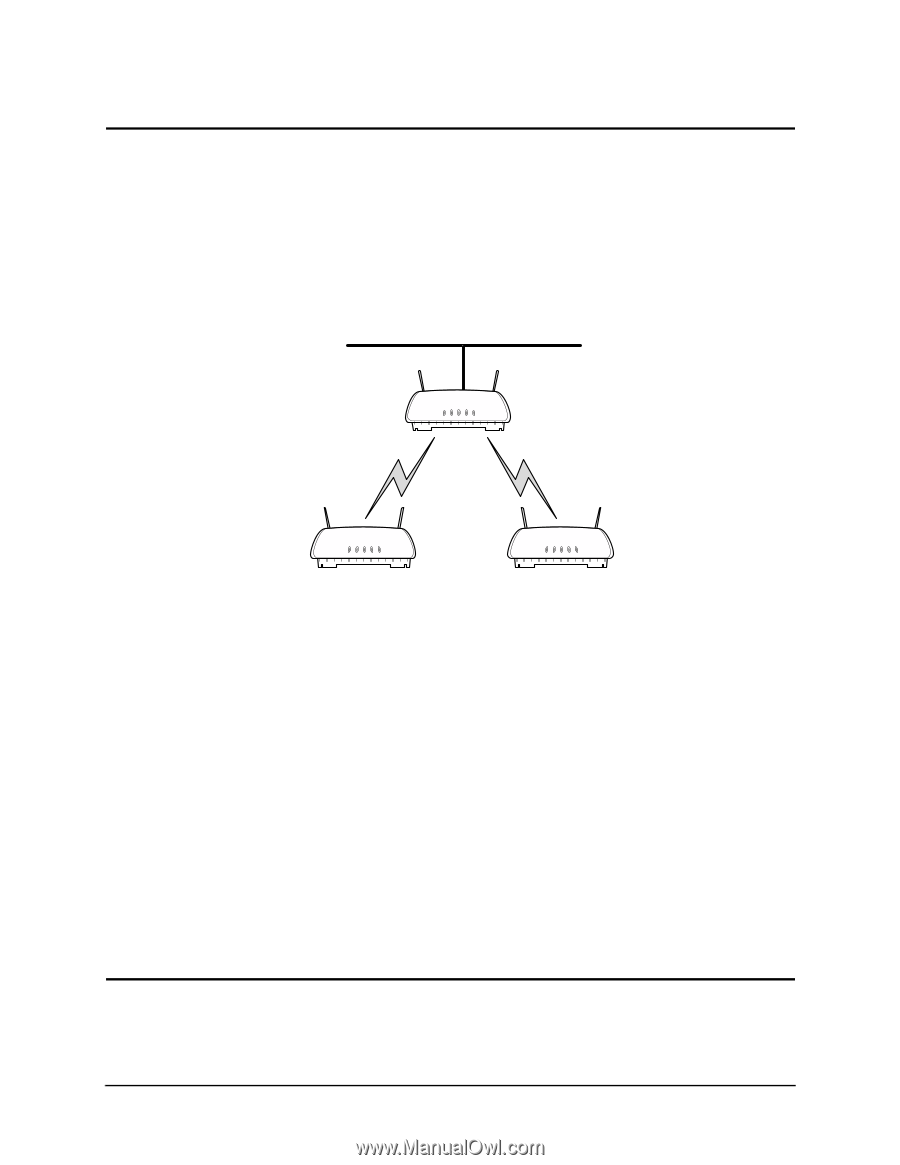
Chapter 1. Introduction This document describes how to set up an Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011/2011B LAN Access Point. For the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN Access Point, the firmware is version 3.x. For the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Access Point, the firmware is version 2.5x. The features in the access point firmware allow network communication between access points. You can use access points to extend radio coverage of a single Ethernet network or to bridge two Ethernet networks. A wireless network consists of a root Wireless Access Point (WLAP) and one or more designated WLAPs. The root access point is typically connected to the Ethernet network; although, this is not a requirement. The network in Figure 1-1 uses two access points operating in the wireless mode to extend radio coverage. The solid line in the figure represents an Ethernet network. A B C Figure 1-1: Extending Network Radio Coverage Using Wireless Access Points Access points maintain their wireless connections through the radio broadcasting of probe, beacon, and Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) messages. Probe and beacon messages are part of the 802.11 protocol. BPDU messages are part of the Spanning Tree Protocol. At the start of a wireless connection, access points send out probe requests and probe responses to gather operating status of other access points. Designated WLAPs also send out probes if they lose the beacon message from the root access point. The beacon messages are broadcast by the access points to keep the network synchronized. It contains information such as the access point's Extended Service Set Identifier (ESS ID) and MAC address. The ESS ID is also called the Network Name or SSID. There are two types of BPDU messages. One type is a configuration BPDU. At the start of the wireless connection, the configuration BPDU messages determine the network configuration for the root access point and designated WLAPs. The other type of BPDU is the WLAP-Alive. These messages keep track of access points operating in the wireless network. The procedures and examples in this document are for Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 and 2011B LAN Access Points with firmware version 2.5x or higher. Additional information on access points is available in the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011/2011B LAN Point Product Reference Guides available on the Intel support web site at www.support.Intel.com. 1.1 Basic Settings for Access Points For a wireless Access Point (AP) operation, make sure that all access points have: • The same ESS ID (Net ID) on the Access Point Installation screen. An example screen is Configuring Access Point Bridging and Repeating (WLAP Mode) 1