TP-Link T1500G-8T T1500G-10PSUN V1 User Guide - Page 158
Network Security
 |
View all TP-Link T1500G-8T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 158 highlights
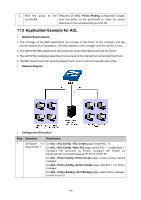
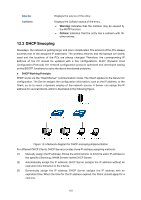
Chapter 12 Network Security Network Security module is to provide the multiple protection measures for the network security, including five submenus: IP-MAC Binding, DHCP Snooping, ARP Inspection, DoS Defend, 802.1X and AAA. Please configure the functions appropriate to your need. 12.1 IP-MAC Binding The IP-MAC Binding function allows you to bind the IP address, MAC address, VLAN ID and the connected Port number of the Host together. Basing on the IP-MAC binding table, ARP Inspection and IP Source Guard functions can control the network access and only allow the Hosts matching the bound entries to access the network. The following three IP-MAC Binding methods are supported by the switch. (1) Manually: You can manually bind the IP address, MAC address, VLAN ID and the Port number together in the condition that you have got the related information of the Hosts in the LAN. (2) Scanning: You can quickly get the information of the IP address, MAC address, VLAN ID and the connected port number of the Hosts in the LAN via the ARP Scanning function, and bind them conveniently. You are only requested to enter the IP address on the ARP Scanning page for the scanning. (3) DHCP Snooping: You can use DHCP Snooping functions to monitor the process of the Host obtaining the IP address from DHCP server, and record the IP address, MAC address, VLAN and the connected Port number of the Host for automatic binding. These three methods are also considered as the sources of the IP-MAC Binding entries. The entries from various sources should be different from one another to avoid collision. Among the entries in collision, only the entry from the source with the highest priority will take effect. These three sources (Manual, Scanning and Snooping) are in descending order of priority. The IP-MAC Binding function is implemented on the Binding Table, Manual Binding and ARP Scanning pages. 12.1.1 Binding Table On this page, you can view the information of the bound entries. 148