TP-Link T1500G-8T T1500G-10PSUN V1 User Guide - Page 177
DoS Attack Type, Description, Network Security, DoS Defend, Defend Config
 |
View all TP-Link T1500G-8T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 177 highlights
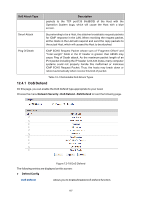
DoS Attack Type Description packets to the TCP port139 (NetBIOS) of the Host with the Operation System bugs, which will cause the Host with a blue screen. Smurf Attack By pretending to be a Host, the attacker broadcasts request packets for ICMP response in the LAN. When receiving the request packet, all the Hosts in the LAN will respond and send the reply packets to the actual Host, which will causes this Host to be attacked. Ping Of Death ICMP ECHO Request Packet whose sum of "Fragment Offset" and "Total Length" fields in the IP header is greater than 65535 may cause Ping of Death attack. As the maximum packet length of an IPv4 packet including the IP header is 65,535 bytes, many computer systems could not properly handle this malformed or malicious ICMP ECHO Request Packet. Thus, the hosts may break down or reboot automatically when receive this kind of packet. Table 12-1 Defendable DoS Attack Types 12.4.1 DoS Defend On this page, you can enable the DoS Defend type appropriate to your need. Choose the menu Network Security→DoS Defend→DoS Defend to load the following page. Figure 12-18 DoS Defend The following entries are displayed on this screen: Defend Config DoS Defend: Allows you to Enable/Disable DoS Defend function. 167