TP-Link T1500G-8T T1500G-10PSUN V1 User Guide - Page 61
LACP Config
 |
View all TP-Link T1500G-8T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
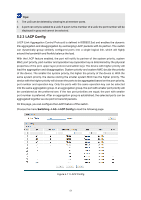
Tips: 1. The LAG can be deleted by clearing its all member ports. 2. A port can only be added to a LAG. If a port is the member of a LAG, the port number will be displayed in gray and cannot be selected. 5.2.3 LACP Config LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is defined in IEEE802.3ad and enables the dynamic link aggregation and disaggregation by exchanging LACP packets with its partner. The switch can dynamically group similarly configured ports into a single logical link, which will highly extend the bandwidth and flexibly balance the load. With the LACP feature enabled, the port will notify its partner of the system priority, system MAC, port priority, port number and operation key (operation key is determined by the physical properties of the port, upper layer protocol and admin key). The device with higher priority will lead the aggregation and disaggregation. System priority and system MAC decide the priority of the device. The smaller the system priority, the higher the priority of the device is. With the same system priority, the device owning the smaller system MAC has the higher priority. The device with the higher priority will choose the ports to be aggregated based on the port priority, port number and operation key. Only the ports with the same operation key can be selected into the same aggregation group. In an aggregation group, the port with smaller port priority will be considered as the preferred one. If the two port priorities are equal, the port with smaller port number is preferred. After an aggregation group is established, the selected ports can be aggregated together as one port to transmit packets. On this page, you can configure the LACP feature of the switch. Choose the menu Switching→LAG→LACP Config to load the following page. Figure 5-11 LACP Config 51