TP-Link T2500-28TCTL-SL5428E T2500-28TCUN V1 User Guide - Page 147
DHCP Option, Lease Time option. In DHCP-OFFER and DHCP-ACK message, the DHCP server
 |
View all TP-Link T2500-28TCTL-SL5428E manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 147 highlights
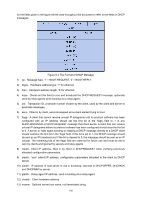
14) file:Boot file name, null terminated string, "generic" name or null in DHCPDISCOVER, fully qualified directory-path name in DHCPOFFER. 15) options:Optional parameters field. See the options documents (RFC 2132) for a list of defined options. We will introduce some familiar options in the next section. DHCP Option This section defines a generalized use of the 'options' field for giving information useful to a wide class of machines, operating systems and configurations. Sites with a single DHCP server that is shared among heterogeneous clients may choose to define other, site-specific formats for the use of the 'options' field. Figure 9-4 gives the format of options field. Figure 9-4 DHCP Option All options begin with a Code octet, which uniquely identifies the option followed by the length octet. The value of the length octet does not include the Code and Length octets. The common options are illustrated as below. 1) option 1:Subnet Mask option. The subnet mask option is option1 which identifies the assigned IP address with network, and its length is 4 octets. 2) option 3:Router option. The router option is option 3 which specifies an IP address for routers on the client's subnet. 3) option 6:DNS option. The DNS option is option 6, and it assigns the IP address of domain name server to the client which allows the client can use the web service in the internet. 4) option 12:Host Name option. The option12 is used to specify the name of the client, which may be requested by the DHCP server for authentication. 5) option 50:Requested IP Address option. The option 50 is used in a DHCP-REQUEST message to allow the client to request the particular IP address. 6) option 51:Lease Time option. In DHCP-OFFER and DHCP-ACK message, the DHCP server uses this option to specify the lease time in which the clients can use the IP address legally. 7) option 53:Message Type option. This option is used to convey the type of the DHCP message. Legal values for this option show in Table 9-1: Value 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Message Type DHCP-DISCOVER DHCP-OFFER DHCP-REQUEST DHCP-DECLINE DHCP-ACK DHCP-NAK DHCP-RELEASE DHCP-INFORM Table 9-1 Option 53 8) option 54:Server Identifier option. DHCP servers include option 54 in the DHCP-OFFER message in order to allow the client to distinguish between lease offers. DHCP clients use the option in a DHCP-REQUEST message to indicate which lease offers is being accepted. 137