TRENDnet TEW-311BRP Manual - Page 63
Access Point, Authentication, Beacon, Interval, Domain Name, Filter, Firewall, Firmware,
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-311BRP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
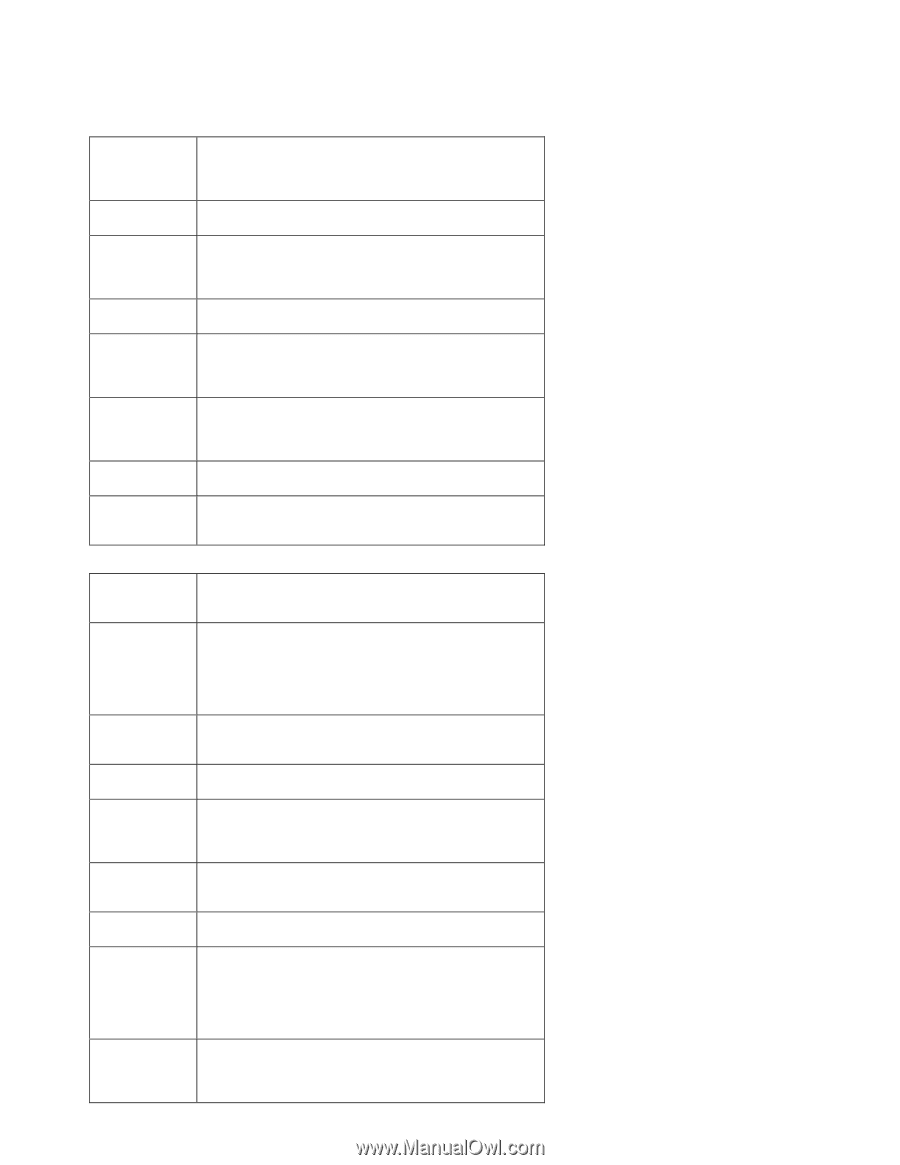
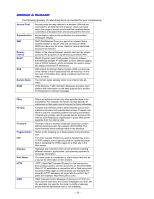
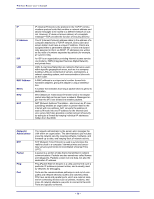
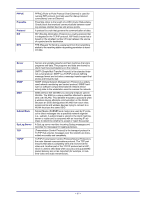
APPENDIX A: GLOSSARY The following glossary of networking terms is provided for your convenience. Access Point Authentication DMZ Beacon Interval DHCP DNS Domain Name DTIM Access points are way stations in a wireless LAN that are connected to an Ethernet hub or server. Users can roam within the range of access points and their wireless device connections are passed from one access point to the next. Authentication refers to the verification of a transmitted message's integrity. DMZ (DeMilitarized Zone) is a part of an network that is located between a secure LAN and an insecure WAN. DMZs provide a way for some clients to have unrestricted access to the Internet. Refers to the interval between packets sent sent by access points for the purposes of synchronizing wireless LANs. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) software automatically assigns IP addresses to client stations logging onto a TCP/IP network, which eliminates the need to manually assign permanent IP addresses. DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS converts machine names to the IP addresses that all machines on the net have. It translates from name to address and from address to name. The domain name typically refers to an Internet site address. DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) provides client stations with information on the next opportunity to monitor for broadcast or multicast messages. Filter Firewall Firmware Fragmentation FTP Gateway Host Name HTTP ICMP Filters are schemes which only allow specified data to be transmitted. For example, the router can filter specific IP addresses so that users cannot connect to those addresses. Firewalls are methods used to keep networks secure from malicious intruders and unauthorized access. Firewalls use filters to prevent unwanted packets from being transmitted. Firewalls are typically used to provide secure access to the Internet while keeping an organization's public Web server separate from the internal LAN. Firmware refers to memory chips that retain their content without electrical power (for example, BIOS ROM). The router firmware stores settings made in the interface. Refers to the breaking up of data packets during transmission. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network, and is typically used for transferring large files or uploading the HTML pages for a Web site to the Web server. Gateways are computers that convert protocols enabling different networks, applications, and operating systems to exchange information. The name given to a computer or client station that acts as a source for information on the network. HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) is the communications protocol used to connect to servers on the World Wide Web. HTTP establishes a connection with a Web server and transmits HTML pages to client browser (for example Windows IE). HTTP addresses all begin with the prefix 'http://' prefix (for example, http://www.yahoo.com). ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a TCP/IP protocol used to send error and control messages over the LAN (for example, it is used by the router to notify a message sender that the destination node is not available). - 55 -