TRENDnet TEW-311BRP Manual - Page 66
Telnet, Virtual Servers, Wireless LAN
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-311BRP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 66 highlights
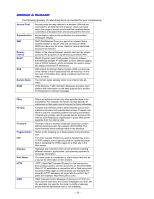
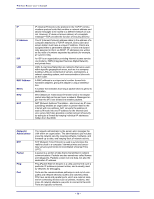
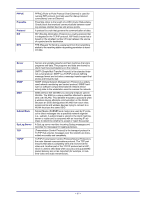
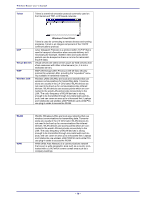
Wireless Router user's manual Telnet Telnet is a terminal emulation protocol commonly used on the Internet and TCP- or IP-based networks: UDP Virtual Servers WEP Wireless LAN Windows Telnet Client Telnet is used for connecting to remote devices and running programs. Telnet is an integral component of the TCP/IP communications protocol. (User Datagram Protocol) is a protocol within TCP/IP that is used to transport information when accurate delivery isn't necessary (for example, realtime video and audio where packets can be dumped as there is no time for retransmitting the data). Virtual servers are client servers (such as Web servers) that share resources with other virtual servers (i.e., it is not a dedicated server). WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is the de facto security protocol for wireless LANs, providing the "equivalent" security available in hardwired networks. Wireless LANs (WLANs) are local area networks that use wireless communications for transmitting data. Transmissions are usually in the 2.4 GHz band. WLAN devices do not need to be lined up for communications like infrared devices. WLAN devices use access points which are connected to the wired LAN and provide connectivity to the LAN. The radio frequency of WLAN devices is strong enough to be transmitted through non-metal walls and objects, and can cover an area up to a thousand feet. Laptops and notebooks use wireless LAN PCMCIA cards while PCs use plug-in cards to access the WLAN. WLAN WAN WLANs (Wireless LANs) are local area networks that use wireless communications for transmitting data. Transmissions are usually in the 2.4 GHz band. WLAN devices do not need to be lined up for communications like infrared devices. WLAN devices use access points which are connected to the wired LAN and provide connectivity to the LAN. The radio frequency of WLAN devices is strong enough to be transmitted through non-metal walls and objects, and can cover an area up to a thousand feet. Laptops and notebooks use wireless LAN PCMCIA cards while PCs use plug-in cards to access the WLAN. WAN (Wide Area Network) is a communications network that covers a wide geographic area such as a country (contrasted with a LAN, which covers a small area such as a company building). - 58 -