Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Reference Guide - Page 100
arcsinh, Numver1, value, List1, squareMatrix1
 |
View all Texas Instruments TINSPIRE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
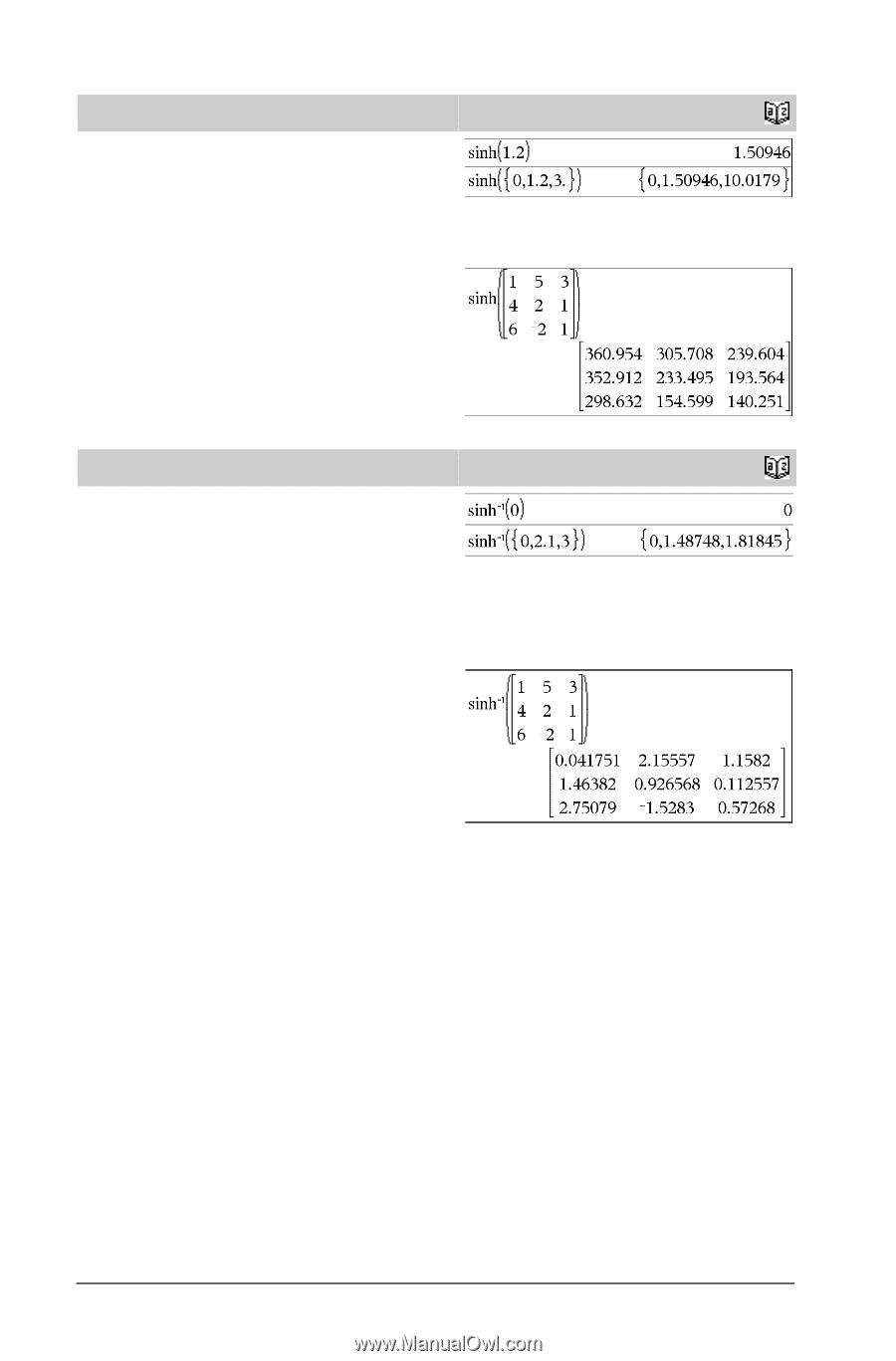
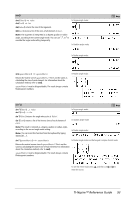
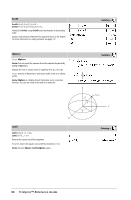
sinh( ) sinh(Numver1) ⇒ value sinh(List1) ⇒ list sinh (Value1) returns the hyperbolic sine of the argument. sinh (List1) returns a list of the hyperbolic sines of each element of List1. sinh(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix In Radian angle mode: Returns the matrix hyperbolic sine of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as calculating the hyperbolic sine of each element. For information about the calculation method, refer to cos(). squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains floating-point numbers. sinh/( ) sinh/(Value1) ⇒ value sinh/(List1) ⇒ list sinh/(Value1) returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of the argument. sinh/(List1) returns a list of the inverse hyperbolic sines of each element of List1. Note: You can insert this function from the keyboard by typing arcsinh(...). sinh/(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix In Radian angle mode: Returns the matrix inverse hyperbolic sine of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as calculating the inverse hyperbolic sine of each element. For information about the calculation method, refer to cos(). squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains floating-point numbers. Catalog > Catalog > 94 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide