Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Reference Guide - Page 94
Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Manual
 |
View all Texas Instruments TINSPIRE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
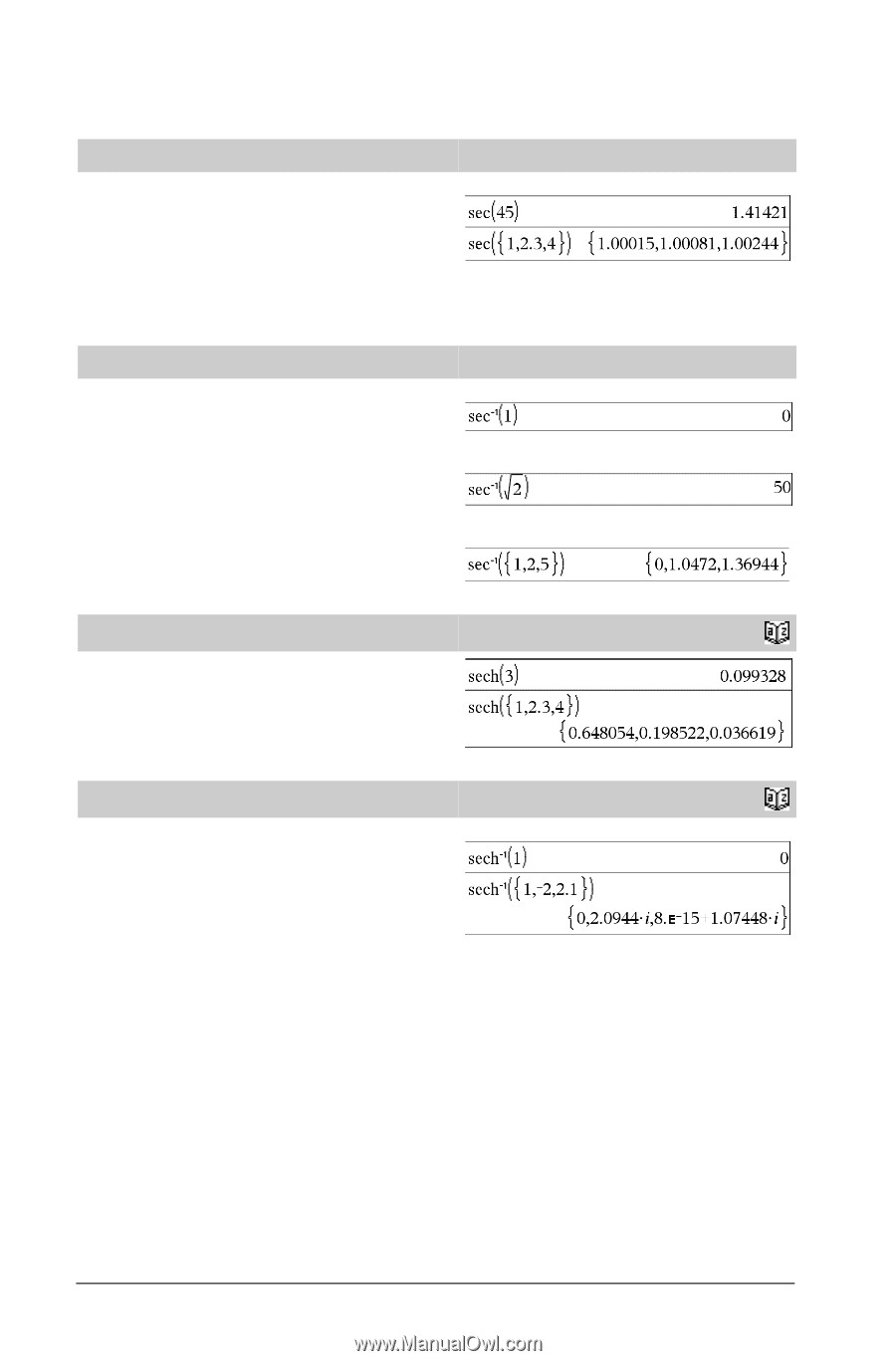
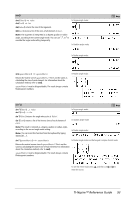
S sec() sec(Value1) ⇒ value sec(List1) ⇒ list In Degree angle mode: Returns the secant of Value1 or returns a list containing the secants of all elements in List1. Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian angle, according to the current angle mode setting. You can use ¡, G, or R to override the angle mode temporarily. sec/() sec/(Value1) ⇒ value sec/(List1) ⇒ list In Degree angle mode: Returns the angle whose secant is Value1 or returns a list containing the inverse secants of each element of List1. Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle, according to the current angle mode setting. In Gradian angle mode: Note: You can insert this function from the keyboard by typing arcsec(...). In Radian angle mode: μ key μ key sech() sech(Value1) ⇒ value sech(List1) ⇒ list Returns the hyperbolic secant of Value1 or returns a list containing the hyperbolic secants of the List1 elements. Catalog > sech/() sech/(Value1) ⇒ value sech/ (List1) ⇒ list Returns the inverse hyperbolic secant of Value1 or returns a list containing the inverse hyperbolic secants of each element of List1. Note: You can insert this function from the keyboard by typing arcsech(...). Catalog > In Radian angle and Rectangular complex mode: 88 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide