Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Reference Guide - Page 37
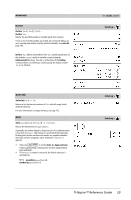
E, Value, Matrix, List1, expression, Vector1, squareMatrix1
 |
View all Texas Instruments TINSPIRE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
4DMS Value 4DMS List 4DMS Matrix 4DMS In Degree angle mode: Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @>DMS. Interprets the argument as an angle and displays the equivalent DMS (DDDDDD¡MM'SS.ss'') number. See ¡, ', '' on page 127 for DMS (degree, minutes, seconds) format. Note: 4DMS will convert from radians to degrees when used in radian mode. If the input is followed by a degree symbol ¡ , no conversion will occur. You can use 4DMS only at the end of an entry line. dotP( ) dotP(List1, List2) ⇒ expression Returns the "dot" product of two lists. dotP(Vector1, Vector2) ⇒ expression Returns the "dot" product of two vectors. Both must be row vectors, or both must be column vectors. E e^() e^(Value1) ⇒ value Returns e raised to the Value1 power. Note: See also e exponent template, page 2. u Note: Pressing to display e^( is different from pressing the E character on the keyboard. You can enter a complex number in rei q polar form. However, use this form in Radian angle mode only; it causes a Domain error in Degree or Gradian angle mode. e^(List1) ⇒ list Returns e raised to the power of each element in List1. e^(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix Returns the matrix exponential of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as calculating e raised to the power of each element. For information about the calculation method, refer to cos(). squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains floating-point numbers. Catalog > Catalog > u key TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 31