Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Reference Guide - Page 20
C, Base16, Catalog >, binomCdf, ceiling
 |
View all Texas Instruments TINSPIRE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
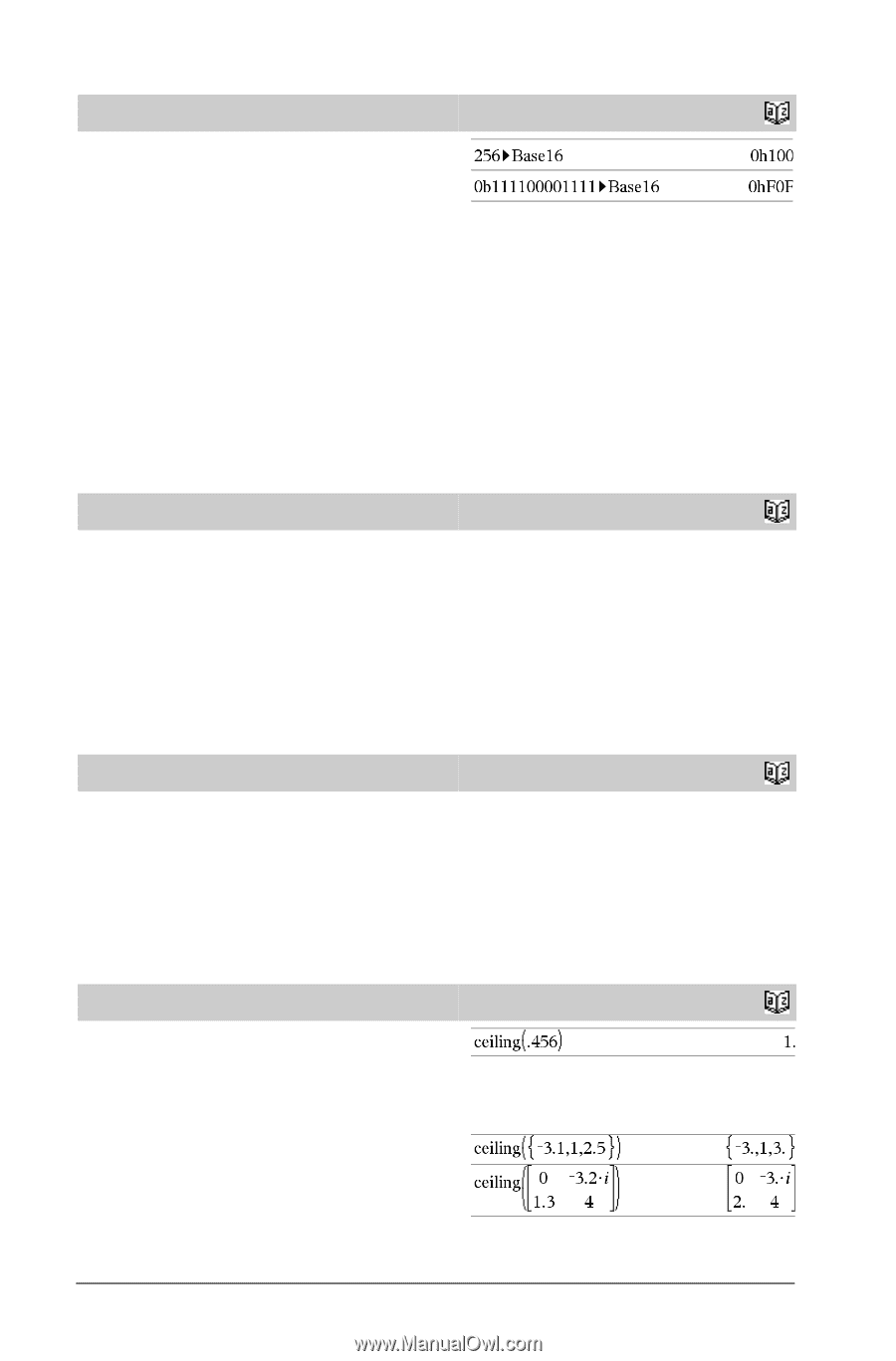
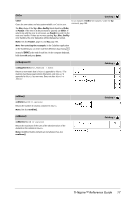
4Base16 Integer1 4Base16 ⇒ integer Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @>Base16. Converts Integer1 to a hexadecimal number. Binary or hexadecimal numbers always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively. 0b binaryNumber 0h hexadecimalNumber Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h. A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can have up to 16. Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal (base 10). The result is displayed in hexadecimal, regardless of the Base mode. If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value into the appropriate range. For more information, see 4Base2, page 12. binomCdf() binomCdf(n,p) ⇒ number binomCdf(n,p,lowBound,upBound) ⇒ number if lowBound and upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists binomCdf(n,p,upBound) for P(0{X{upBound) ⇒ number if upBound is a number, list if upBound is a list Computes a cumulative probability for the discrete binomial distribution with n number of trials and probability p of success on each trial. For P(X { upBound), set lowBound=0 binomPdf() binomPdf(n,p) ⇒ number binomPdf(n,p,XVal) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal is a list Computes a probability for the discrete binomial distribution with n number of trials and probability p of success on each trial. C ceiling( ) ceiling(Value1) ⇒ value Returns the nearest integer that is | the argument. The argument can be a real or a complex number. Note: See also floor(). ceiling(List1) ⇒ list ceiling(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix Returns a list or matrix of the ceiling of each element. 14 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide Catalog > Catalog > Catalog > Catalog >