Texas Instruments TINSPIRE Reference Guide - Page 132
In Degree, Gradian or Radian angle mode
 |
View all Texas Instruments TINSPIRE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 132 highlights
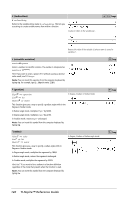
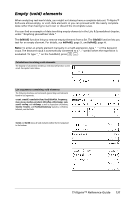
# (indirection) # varNameString Refers to the variable whose name is varNameString. This lets you use strings to create variable names from within a function. Creates or refers to the variable xyz . /k keys Returns the value of the variable (r) whose name is stored in variable s1. E (scientific notation) mantissaEexponent Enters a number in scientific notation. The number is interpreted as mantissa × 10exponent. Hint: If you want to enter a power of 10 without causing a decimal value result, use 10^integer. Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @E. for example, type 2.3@E4 to enter 2.3E4. i key g (gradian) Expr1g ⇒ expression List1g ⇒ list Matrix1g ⇒ matrix In Degree, Gradian or Radian mode: This function gives you a way to specify a gradian angle while in the Degree or Radian mode. In Radian angle mode, multiplies Expr1 by p/200. In Degree angle mode, multiplies Expr1 by g/100. In Gradian mode, returns Expr1 unchanged. Note: You can insert this symbol from the computer keyboard by typing @g. ¹ key R(radian) Value1R ⇒ value List1R ⇒ list Matrix1R ⇒ matrix This function gives you a way to specify a radian angle while in Degree or Gradian mode. In Degree angle mode, multiplies the argument by 180/p. In Radian angle mode, returns the argument unchanged. In Gradian mode, multiplies the argument by 200/p. Hint: Use R if you want to force radians in a function definition regardless of the mode that prevails when the function is used. Note: You can insert this symbol from the computer keyboard by typing @r. In Degree, Gradian or Radian angle mode: ¹ key 126 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide