ZyXEL GS2200-8 User Guide - Page 193
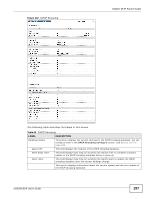
IP Source Guard Static Binding
 |
View all ZyXEL GS2200-8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 193 highlights
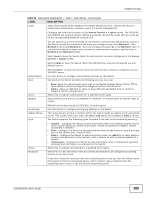
CHAPTER 25 IP Source Guard 25.1 Overview Use IP source guard to filter unauthorized DHCP and ARP packets in your network. IP source guard uses a binding table to distinguish between authorized and unauthorized DHCP and ARP packets in your network. A binding contains these key attributes: • MAC address • VLAN ID • IP address • Port number When the Switch receives a DHCP or ARP packet, it looks up the appropriate MAC address, VLAN ID, IP address, and port number in the binding table. If there is a binding, the Switch forwards the packet. If there is not a binding, the Switch discards the packet. 25.1.1 What You Can Do • Use the IP Source Guard screen (Section 25.2 on page 194) to look at the current bindings for DHCP snooping and ARP inspection. • Use the IP Source Guard Static Binding screen (Section 25.3 on page 195) to manage static bindings for DHCP snooping and ARP inspection. • Use the DHCP Snooping screen (Section 25.4 on page 196) to look at various statistics about the DHCP snooping database. • Use this DHCP Snooping Configure screen (Section 25.5 on page 199) to enable DHCP snooping on the Switch (not on specific VLAN), specify the VLAN where the default DHCP server is located, and configure the DHCP snooping database. • Use the DHCP Snooping Port Configure screen (Section 25.5.1 on page 201) to specify whether ports are trusted or untrusted ports for DHCP snooping. • Use the DHCP Snooping VLAN Configure screen (Section 25.5.2 on page 203) to enable DHCP snooping on each VLAN and to specify whether or not the Switch adds DHCP relay agent option 82 information to DHCP requests that the Switch relays to a DHCP server for each VLAN. • Use the ARP Inspection Status screen (Section 25.6 on page 204) to look at the current list of MAC address filters that were created because the Switch identified an unauthorized ARP packet. • Use the ARP Inspection VLAN Status screen (Section 25.7 on page 205) to look at various statistics about ARP packets in each VLAN. • Use the ARP Inspection Log Status screen (Section 25.8 on page 206) to look at log messages that were generated by ARP packets and that have not been sent to the syslog server yet. • Use the ARP Inspection Configure screen (Section 25.9 on page 207) to enable ARP inspection on the Switch. You can also configure the length of time the Switch stores records of discarded ARP packets and global settings for the ARP inspection log. GS2200-8/24 User's Guide 193