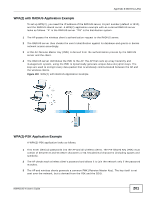
ZyXEL NWA1100 User Guide - Page 196
Ieee 802.1x, Radius, Table 66, Security, Level, Security Type
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA1100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 196 highlights
Appendix E Wireless LANs The following figure shows the relative effectiveness of these wireless security methods available on your NWA. Table 66 Wireless Security Levels SECURITY LEVEL SECURITY TYPE Least Secure Unique SSID (Default) Unique SSID with Hide SSID Enabled MAC Address Filtering WEP Encryption IEEE802.1x EAP with RADIUS Server Authentication Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) WPA2 Most Secure Note: You must enable the same wireless security settings on the NWA and on all wireless clients that you want to associate with it. IEEE 802.1x In June 2001, the IEEE 802.1x standard was designed to extend the features of IEEE 802.11 to support extended authentication as well as providing additional accounting and control features. It is supported by Windows XP and a number of network devices. Some advantages of IEEE 802.1x are: • User based identification that allows for roaming. • Support for RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service, RFC 2138, 2139) for centralized user profile and accounting management on a network RADIUS server. • Support for EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol, RFC 2486) that allows additional authentication methods to be deployed with no changes to the access point or the wireless clients. RADIUS RADIUS is based on a client-server model that supports authentication, authorization and accounting. The access point is the client and the server is the RADIUS server. The RADIUS server handles the following tasks: • Authentication Determines the identity of the users. • Authorization Determines the network services available to authenticated users once they are connected to the network. • Accounting Keeps track of the client's network activity. 196 NWA1100-N User's Guide