ZyXEL P-871H User Guide - Page 44
Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
 |
View all ZyXEL P-871H manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
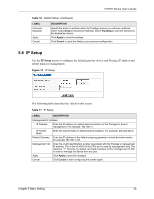
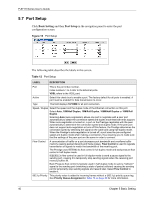
P-871H Series User's Guide CHAPTER 6 VLAN The type of screen you see here depends on the VLAN Type you selected in the Prestige Setup screen. This chapter shows you how to configure 802.1Q tagged and port-based VLANs. 6.1 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN A tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identify the VLAN membership of a frame across bridges - they are not confined to the Prestige on which they were created. The VLANs can be created statically by hand or dynamically through GVRP. The VLAN ID associates a frame with a specific VLAN and provides the information that the Prestige needs to process the frame across the network. A tagged frame is four bytes longer than an untagged frame and contains two bytes of TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier, residing within the type/length field of the Ethernet frame) and two bytes of TCI (Tag Control Information, starts after the source address field of the Ethernet frame). The CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) is a single-bit flag, always set to zero for Ethernet devices. If a frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not be forwarded as it is to an untagged port. The remaining twelve bits define the VLAN ID, giving a possible maximum number of 4,096 (212) VLANs. Note that user priority and VLAN ID are independent of each other. A frame with VID (VLAN Identifier) of null (0) is called a priority frame, meaning that only the priority level is significant and the default VID of the ingress port is given as the VID of the frame. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is used to identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN configurations are 4,094. TPID User Priority 2 Bytes 3 Bits CFI VLAN ID 1 Bit 12 bits 6.1.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames Each port on the Prestige is capable of passing tagged or untagged frames. To forward a frame from an 802.1Q VLAN-aware Prestige to an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware Prestige, the Prestige first decides where to forward the frame and then strips off the VLAN tag. To forward a frame from an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware Prestige to an 802.1Q VLAN-aware Prestige, the Prestige first decides where to forward the frame, and then inserts a VLAN tag reflecting the ingress port's default VID. The default PVID is VLAN 1 for all ports, but this can be changed. Chapter 6 VLAN 43