Onkyo HT-R640 Owner Manual - Page 31
Connecting Components with HDMI - hdmi version
 |
View all Onkyo HT-R640 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
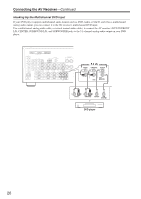
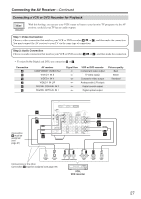
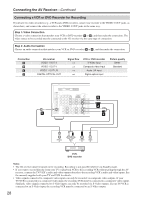
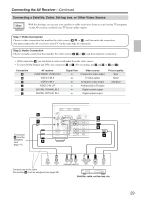
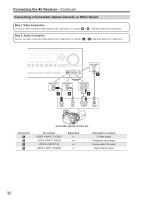
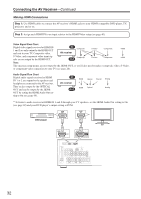
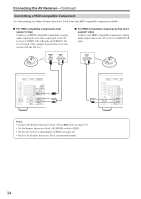
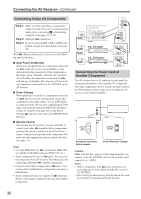
Connecting the AV Receiver-Continued Connecting Components with HDMI About HDMI Designed to meet the demands of digital TV, HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is a new digital interface standard for connecting TVs, projectors, DVD players, set-top boxes, and other video components. Until now, several separate video and audio cables have been required to connect AV components. With HDMI, a single cable can carry control signals, digital video, and up to eight channels of digital audio (2-channel PCM, multichannel digital audio, and multichannel PCM). The HDMI video stream (i.e., video signal) is compatible with DVI (Digital Visual Interface)*1, so TVs and displays with a DVI input can be connected by using an HDMI-to-DVI adapter cable. (This may not work with some TVs and displays, resulting in no picture.) The AV receiver uses HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection), so only HDCP-compatible components can display the picture. The AV receiver's HDMI interface is based on the following standard: High-Definition Multimedia Interface Specification Informational Version 1.1 Supported Audio Formats • 2-channel linear PCM (32-192 kHz, 16/20/24 bit) • Multichannel linear PCM (5.1 ch, 32-96 kHz, 16/20/24 bit) • Bitstream (Dolby Digital, DTS) Your DVD player must also support HDMI output of the above audio formats. About Copyright Protection The AV receiver supports HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection)*2, a copy-protection system for digital video signals. Other devices connected to the AV receiver via HDMI must also support HDCP. Commercially available HDMI cables (supplied with some components) should be used to connect the AV receiver's HDMI OUT to the HDMI input on your TV or projector. *1 DVI (Digital Visual Interface): The digital display interface standard set by the DDWG*3 in 1999. *2 HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection): The video encryption technology developed by Intel for HDMI/DVI. It's designed to protect video content and requires a HDCP-compatible device to display the encrypted video. *3 DDWG (Digital Display Working Group): Lead by Intel, Compaq, Fujitsu, Hewlett Packard, IBM, NEC, and Silicon Image, this open industry group's objective is to address the industry's requirements for a digital connectivity specification for high-performance PCs and digital displays. 31