D-Link DSL-504T Product Manual - Page 88
IP Address Setup continued
 |
UPC - 790069265204
View all D-Link DSL-504T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 88 highlights
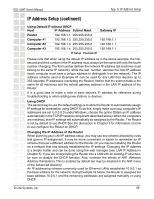
DSL-504T User's Manual App. A: IP Address Setup IP Address Setup (continued) Using Default IP without DHCP Host IP Address Subnet Mask Router 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Computer #1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 Computer #2 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 Computer #3 192.168.1.4 255.255.255.0 IP Setup - Example #1 Gateway IP 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.1 Please note that when using the default IP address as in the above example, the first, second and third number in the IP address must always be the same with only the fourth number changing. The first number defines the network IP address (all machines must belong to the same IP network), while the last number denotes the host IP address (each computer must have a unique address to distinguish it on the network). The IP address scheme used in Example #1 can be used for any LAN that requires up to 253 separate IP addresses (excluding the Router). Notice that the subnet mask is the same for all machines and the default gateway address is the LAN IP address of the Router. It is a good idea to make a note of each device's IP address for reference during troubleshooting or when adding new stations or devices. Using DHCP The second way to use the default settings is to allow the Router to automatically assign IP settings for workstation using DHCP. To do this, simply make sure your computer's IP addresses are set to 0.0.0.0 (under Windows, choose the option Obtain an IP address automatically in the TCP/IP network component described above). When the computers are restarted, their IP settings will automatically be assigned by the Router. The Router is set by default to use DHCP. See the discussion in Chapter 3 for information on how to use configure the Router for DHCP. Changing the IP Address of the Router When planning your LAN IP address setup, you may use any scheme allowed by rules that govern IP assignment. It may be more convenient or easier to remember an IP scheme that use a different address for the Router. Or you may be installing the Router on a network that has already established the IP settings. Changing the IP address is a simple matter and can be done using the web manager (see LAN IP Address in Chapter 5). If you are incorporating the Router into a LAN with an existing IP structure, be sure to disable the DHCP function. Also, consider the effects of NAT (Network Address Translation). This is enabled by default but may be disabled in the NAT menu of the Advanced directory. An IP addressing scheme commonly used for Ethernet LANs establishes 10.0.0.1 as the base address for the network. Using Example #2 below, the Router is assigned the base address 10.0.0.1 and the remaining addresses are assigned manually or using DHCP. D-Link Systems, Inc. 88