HP T5125 Administrator's Guide: HP Compaq t5125/t5135 Thin Clients, build S1ST - Page 39
Prerequisites, Procedural overview, Configuring a network environment
 |
UPC - 082960980097
View all HP T5125 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
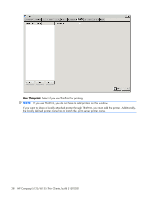
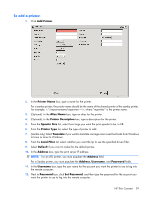
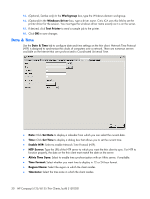
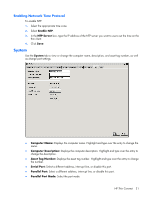
Capture tool from within the t5135 image (see Management on page 22 for more information about ThinState). ThinState will capture a file named profile.ini and save that file onto a USB storage device. Access the USB storage device and change the name of the config.ini file to global.ini. After renaming the file, place in the FTPROOT/HP folder on your Microsoft Windows Server or Linux FTP server. The global.ini file contains the settings that will be propagated onto all thin clients connected to the FTP server. Every setting on the t5135 can be configured with this file, including screen size, application to connect to (such as RDP/ICA connections), security, keyboard settings, Altiris server information, WOL and VNC settings, etc. User profile.ini files are created exactly the same way as global.ini files. After capturing the config.ini using ThinState Capture, rename the config.ini to the specific name for each specific user. User profile.ini files are used to override specific global.ini settings or add different settings for an individual user. See the following for instructions for where to place the global.ini and user profile.ini files. Prerequisites ● Windows Server 2000, Windows Server 2003, or Linux Server system up and running. ● DHCP server up and running. ● Domain Controller/Active Directory. Domain Controller/Active Directory is only required if accessing the global and user profile .ini files on the FTP server requires domain authentication instead of anonymous access. For more information, see the Note section. HP recommends for future use with ICA and RDP. Procedural overview NOTE: The following procedure is for Windows 2003 Server. The steps for Windows 2000 Server and Windows 2003 Server may vary slightly. This section provides a quick overview of the steps required to complete the configuration. 1. Set up an FTP Server in Windows Server 2003 a. Install Internet Information Services (IIS) and the FTP Service b. Configure the FTP service to allow only anonymous connections 2. Set up shared directories to access the HP-format global profile .ini file & user profile .ini files a. Obtain an HP-format global profile .ini file b. Configure shared directories. 3. Configure a DHCP server Configuring a network environment 1. Set up an FTP server in Windows Server 2003. Because FTP depends on Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), IIS and the FTP service must be installed on the computer. To install IIS and the FTP Service: a. Install Internet Information Services and the FTP service: 1. Click Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs. 2. Click Add/Remove Windows Components. Network Mode (Stateless) FTP/DHCP server and profile setup 33