TP-Link 13dBi CPE510 V1 UG - Page 50
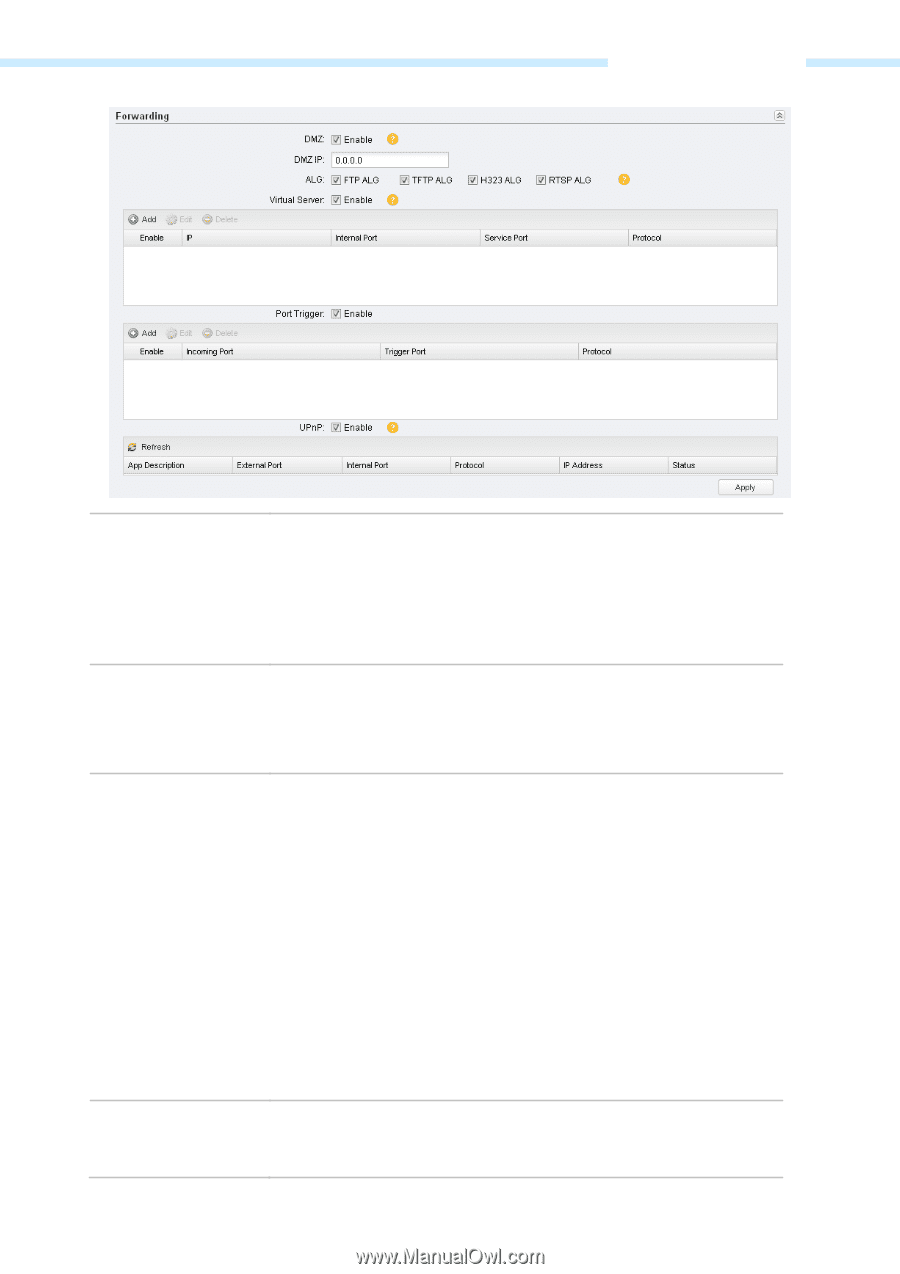
DMZ IP, Virtual Server, Enable, FTP ALG, H323 ALG
 |
View all TP-Link 13dBi manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
Chapter 5 Network Tab DMZ DMZ IP ALG Virtual Server Check the Enable box to use the DMZ function. DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one computer/device behind NAT to become "demilitarized", so all packets from the external network are forwarded to this computer/device. The demilitarized host is exposed to the wide area network, which can realize the unlimited bidirectional communication between internal hosts and external hosts. Specify the IP address of the local host network device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed to the external network. Any PC that was used for a DMZ must have a static or reserved IP Address because its IP Address may change when using the DHCP function. Common NAT only translates the address of packets at network layer and the port number at transport layer but cannot deal with the packets with embedded source/destination information in the application layer. Application layer gateway (ALG) can deal with protocols with embedded source/destination information in the application payload. Some protocols such as FTP, TFTP, H323 and RTSP require ALG (Application Layer Gateway) support to pass through NAT. FTP ALG - Allows FTP clients and servers to transfer data across NAT. TFTP ALG - Allows TFTP clients and servers to transfer data across NAT. H323 ALG - Allows Microsoft NetMeeting clients to communicate across NAT. RTSP ALG - Allows some media player clients to communicate with some streaming media servers across NAT. Check the Enable box to use the virtual server function. Virtual servers can be used for setting up public services on your local area network, such as DNS, Email and FTP. A virtual server is defined as a service port, and all requests from - 47 -