TP-Link 13dBi CPE510 V1 UG - Page 61
Wireless Basic Settings, Wireless Tab - cpe510 5ghz
 |
View all TP-Link 13dBi manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
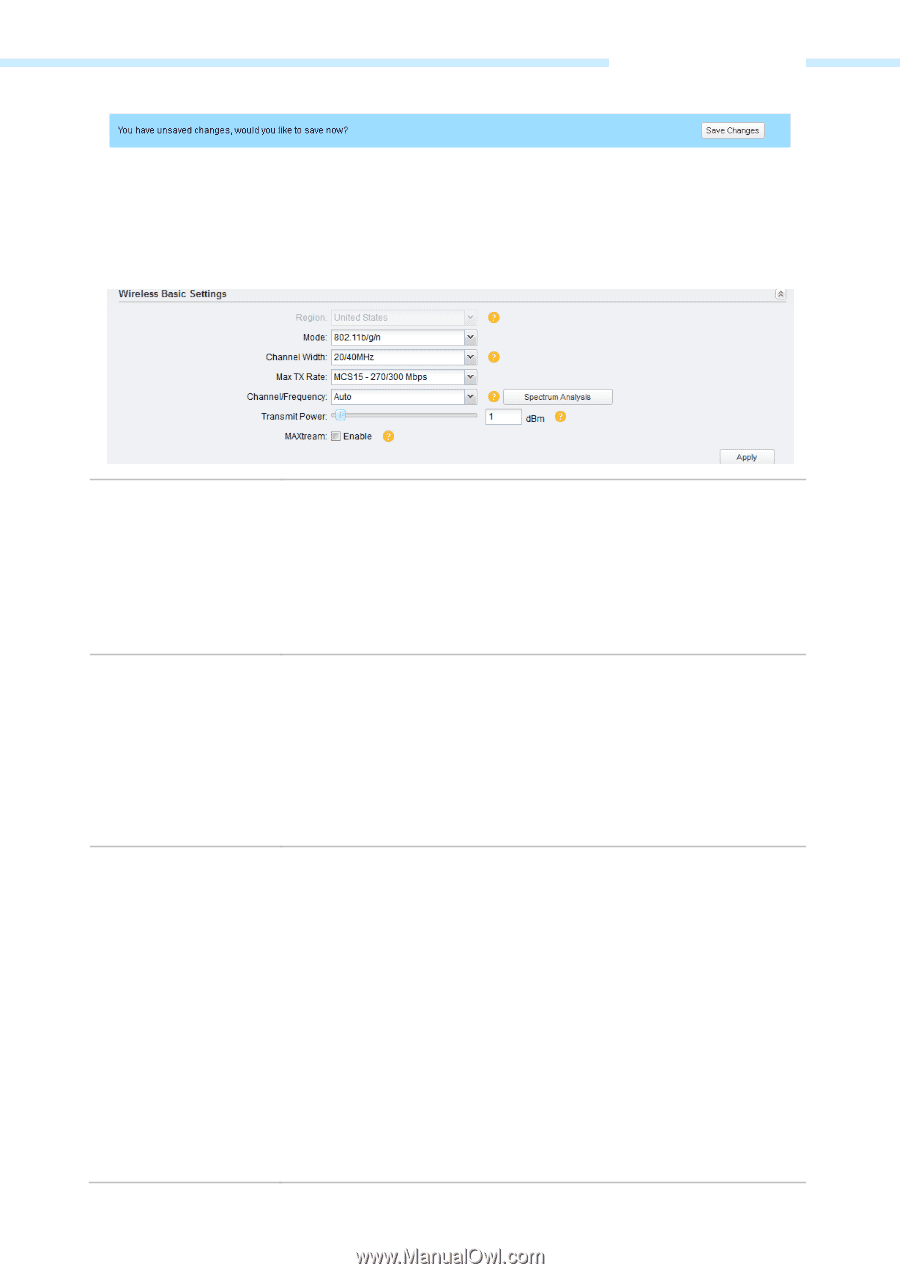
Chapter 6 Wireless Tab Wireless Basic Settings This section allows you to configure wireless basic settings, such as region, 802.11 mode, Transmit Power, and data rates. Region Mode Channel Width Select your region from the drop-down list and agree to the Terms of Use in the pop-up window. Available frequency channels and maximum transmit power may vary across different countries. NOTE: Ensure you select a certain country to comply with local laws. Incorrect settings may cause interference. Limited to local law of the United States, the checkbox of region is not selectable. Select the protocol standard used in the wireless network. With a frequency band of 2.4GHz, CPE210/CPE220/BS210/OAP210 supports five wireless modes: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11b/g and 802.11b/g/n. You are recommended to set the 11b/g/n mixed mode, and all of 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the device. CPE510/CPE520/BS510 has a frequency band of 5GHz, supporting 802.11a, 802.11n and 802.11a/n modes. We suggest to set in 11a/n mode, allowing both 802.11a and 802.11n wireless stations to access the device. Select the channel width of this device. Options include 5MHz, 10MHz, 20MHz and 20/40MHz (this device automatically selects 20MHz or 40MHz, and 20MHz will be used if 40MHz is not available). Users select corresponding channel width according to whether their devices support it. According to IEEE 802.11n standard, using a channel width of 40MHz can increase wireless throughput. However, users may choose lower bandwidth due to the following reasons: 1. Increase the available number of channels within the limited total bandwidth. 2. To avoid interference from overlapping channels occupied by other devices in the environment. 3. Lower bandwidth can concentrate higher transmit power, increasing stability of wireless links over long distances. 4. Subject to the channel width of root AP in Client/ Bridge/ Repeater/ Client Router operation modes. - 58 -