D-Link DES-3226SM Product Manual - Page 76
Configuring QoS Output Scheduling, NOTICE, config scheduling, QoS Output Scheduling
 |
UPC - 790069247118
View all D-Link DES-3226SM manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 76 highlights
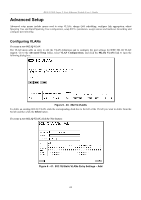
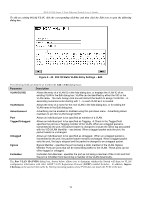
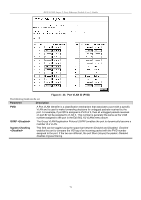
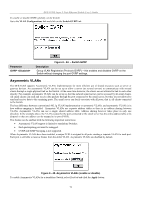
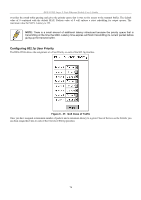
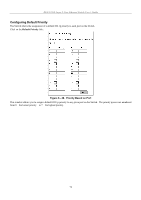
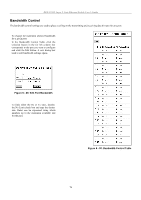
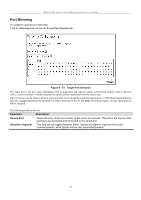
DES-3226S Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch User's Guide Configure QoS (Quality of Service) The DES-3226S Switch supports 802.1p priority queuing. The Switch has 4 priority queues. These priority queues are numbered from 0 (Class 0) - the lowest priority queue - to 3 (Class 3) - the highest priority queue. The eight priority queues specified in IEEE 802.1p (p0 to p7) are mapped to the Switch's priority queues as follows: • p1 and p2 are assigned to the Switch's Class 0 queue. • p0 and p3 are assigned to the Switch's Class 1 queue. • p4 and p5 are assigned to the Switch's Class 2 queue. • p6 and p7 are assigned to the Switch's Class 3 queue. Priority scheduling is implemented using two types of methods, strict priority and round-robin priority. If no changes are made to the QoS priority scheduling settings the method used is strict priority. For strict priority-based scheduling, packets residing in the higher priority queues are transmitted first. Only when these queues are empty, are packets of lower priority allowed to be transmitted. Higher priority packets always receive preference regardless of the amount of lower priority packets in the buffer and regardless of the time elapsed since any lower priority packets have been transmitted. By default the Switch is configured to empty the buffer using strict priority. NOTICE: The default QoS scheduling arrangement is a strict priority schedule. To customize scheduling to set up round-robin queue clearing, the MAX. Latency and MAX. Packets values need to be changed using the config scheduling command. See config scheduling below. To use implement round-robin (weighted) priority, the Switch's four priority queues can be configured to reduce the buffer in a round-robin fashion - beginning with the highest priority queue, and proceeding to the lowest priority queue before returning to the highest priority queue. The weighted-priority based scheduling alleviates the main disadvantage of strict priority-based scheduling − in that lower priority queues get starved of bandwidth − by providing a minimum bandwidth to all queues for transmission. This is accomplished by configuring the maximum number of packets allowed to be transmitted from a given priority queue and the maximum amount of time a given priority queue will have to wait before being allowed to transmit its accumulated packets. This establishes a Class of Service (CoS) for each of the Switch's four hardware priority queues. The possible range for maximum packets is: 0 to 255 packets. The possible range for maximum latency is: 0 to 255 (in increments of 16 microseconds each). Remember that the DES-3226S has four priority queues (and thus four Classes of Service) for each port on the Switch. Configuring QoS Output Scheduling Click the Configure QoS link on the Advanced Setup menu, and the click on the QoS Output Scheduling link: Figure 6 - 46. QoS Output Scheduling The MAX. Packets field specifies the number of packets that a queue will transmit before surrendering the transmit buffer to the next lower priority queue in a round-robin fashion. The default value of 0 combined with the default MAX. Latency value of 0 will enforce a strict scheduling for output queues. The maximum value for MAX. Packets is 255. The MAX. Latency field specifies the maximum amount of time-in multiples of 16 microseconds-that a queue will have to wait before being given access to the transmit buffer. The MAX. Latency is a priority queue timer. When it expires, it 73