HP StorageWorks 8/80 Brocade Access Gateway Administrator's Guide v6.2.0 (53-1 - Page 20
Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
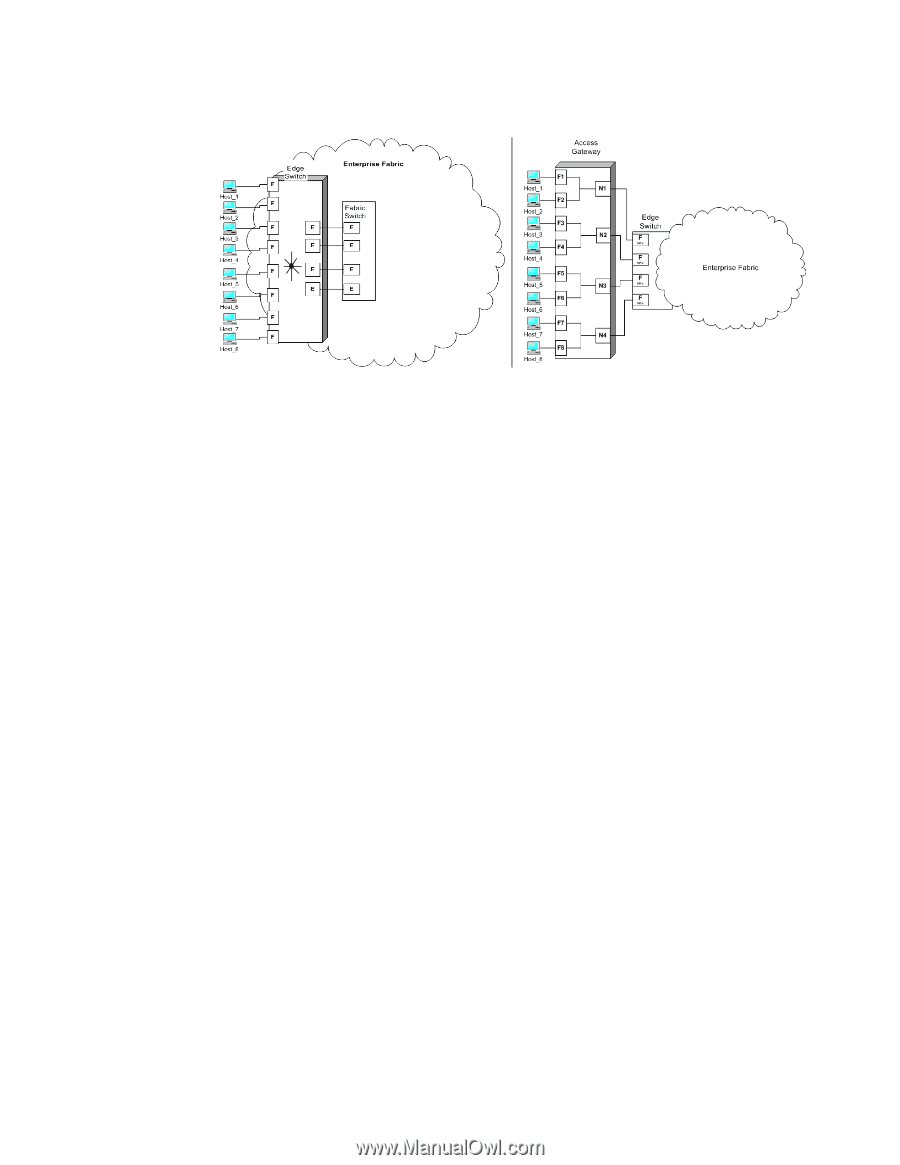
1 Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode FIGURE 1 Access Gateway and fabric switch comparison The following points summarize the differences between a Fabric OS switch in Native mode and a Fabric OS switch in AG mode: • The Fabric OS switch in Native mode is a part of the fabric; it requires two to four times as many physical ports, consumes fabric resources, and can connect to a Fabric OS fabric only. • A switch in AG mode is outside of the fabric; it reduces the number of switches in the fabric and the number of required physical ports. You can connect an AG switch to either a Fabric OS, M-EOS, or Cisco-based fabric. Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode When a switch is behaving as an Access Gateway, RBAC features in Fabric OS are available, but Admin Domains, Advanced Performance Monitoring, direct connection to SAN target devices, Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop support, FICON, IP over FC, extended fabrics, management platform services, name services (SNS), port mirroring, SMI-S, and zoning are not available or no longer applicable. Table 1 lists Fabric OS components that are supported on a switch when AG mode is enabled. "No" indicates that the feature is not provided in AG mode. "NA" indicates this feature is not applicable in Access Gateway mode of operation. A single asterisk (*) indicates the feature is transparent to AG, that is AG forwards the request to the Enterprise fabric. Two asterisks (**) indicates that if the Enterprise fabric is not a Brocade fabric, the feature may not be available. Security enforcement can be done in either the Enterprise fabric using the DCC policy or in the Access Gateway module using Advanced Device Security (ADS) policy. The ADS policy secures virtual and physical connections to the SAN. When you enable the ADS policy, by default, every F_Port is configured to allow all devices to login or be a part of the Access List. The Allow list restricts the devices that can log into a specific F_Port. Because all WWNs are a part of the Access List, you can identify which devices are allowed to log in on a per F_Port basis by specifying the device's port WWN(PWWN). See the Fabric Command Reference on using the ag --adsset command to set the "Allow List" to All Access or No Access. Alternatively the security policy can be established in the Enterprise fabric. For information on the ADS policy, see "Setting which devices can log in if ADS policy is enabled" on page 10 or "Setting which devices cannot log in if ADS policy is enabled" on page 11. 2 Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 53-1001189-01