HP StorageWorks 8/80 Brocade Access Gateway Administrator's Guide v6.2.0 (53-1 - Page 32
Failover policy
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
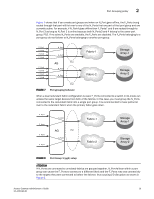
2 Failover policy Failover policy Access Gateway Failover and Failback policies ensure maximum uptime for the servers. When a port is configured as an N_Port and if by default, the Failover policy is enabled, F_Ports are not disabled if its N_Port goes off line. If you specify a Preferred Secondary N_Port for any of the F_Ports, and if the N_Port goes offline, the F_Ports will fail over to the Preferred Secondary N_Port, and then re-enable. The specified Preferred Secondary N_Port must be online; otherwise, the F_Ports will become disabled. Alternatively, if a Preferred Secondary N_Port is not set for any of F_Ports, the F_Ports will fail over to other online N_Ports belonging to the same N_Port group, and then re-enable. The FLOGI and FDISC requests are forwarded from F_Ports through the new N_Port. If multiple N_Ports are available as candidates for failover, Access Gateway selects one or more N_Ports so that the F_Ports are evenly balanced across all the N_Ports. NOTE Failover of F_Ports to new a N_Port generates a RASLOG message. The Failover policy allows hosts to automatically remap to an online N_Port if the primary N_Port goes offline. The Failover policy is enabled (or enforced) during power-up. The Failover policy evenly distributes the F_Ports that are mapped to an offline N_Port among all the online N_Ports. The Failover policy is a parameter of each N_Port. By default, the Failover policy is enabled for all N_Ports. The following sequence describes how a failover event occurs: • An N_Port goes offline. • All F_Ports mapped to that N_Port are disabled. • If the N_Port Failover policy is enabled, and a Preferred Secondary N_Port is specified for the F_Port and that N_Port is online, the F_Port fails over to the respective Preferred Secondary N_Port, and then re-enables. NOTE The Preferred Secondary N_Port is defined per F_Port. For example, if two F_Ports are mapped to a primary N_Port1, you can define a secondary N_Port for one of those F_Ports and not define a secondary N_Port for the other F_Port. Typically, this is done by the server administrator. You must determine whether you want to define a preferred secondary map for each of the servers or just a subset of the servers. • If the Preferred Secondary N_Port is not online, those F_Ports are disabled. • If the Preferred Secondary N_Port is not set for any of the F_Ports, those F_Ports will fail over to other available N_Ports belonging to the same N_Port group, and then re-enable. • The host establishes a new connection with the fabric. Example: Failover Policy This example shows the failover behavior in a scenario where two fabric ports go offline, one after the other. Note that this example assumes that no Preferred Secondary N_Port is set for any of the F_Ports. • First the Edge switch F_A1 port goes offline, as shown in Figure 4 on page 15 Example 1 (left), causing the corresponding Access Gateway N_1 port to be disabled. The ports mapped to N_1 fail over; F_1 fails over to N_2 and F_2 fails over to N_3. 14 Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 53-1001189-01