HP StorageWorks 8/80 Brocade Access Gateway Administrator's Guide v6.2.0 (53-1 - Page 23
How Access Gateway maps ports
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
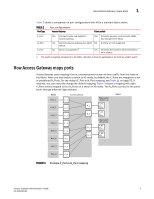
How Access Gateway maps ports 1 Table 2 shows a comparison of port configurations with AG to a standard fabric switch. TABLE 2 Port Type Port configurations Access Gateway Fabric switch F_Port N_Port E_Port Yes Connects hosts and targets to Access Gateway. Yes Connects devices, such as hosts, HBAs, and storage to the fabric. Yes Connects Access Gateway to a fabric NA N_Ports are not supported. switch. NA ISL is not supported.1 Yes Connects the switch to other switches to form a fabric. 1. The switch is logically transparent to the fabric, therefore it does not participate in the SAN as a fabric switch. How Access Gateway maps ports Access Gateway uses mapping-that is, pre-provisioned routes-to direct traffic from the hosts to the fabric. When you first enable a switch to AG mode, by default, the F_Ports are mapped to a set of predefined N_Ports. For the default F_Port-to-N_Port mapping, see Table 11 on page 53. If required, you can manually change the default mapping. Figure 3 shows a mapping with eight F_Ports evenly mapped to four N_Ports on a switch in AG mode. The N_Ports connect to the same fabric through different Edge switches. Hosts Host_1 Host_2 Host_3 Access Gateway F_1 N_1 F_2 N_2 F_3 Edge Switch (Switch_A) F_A1 NPIV enabled F_A2 NPIV enabled Fabric Host_4 F_4 Host_5 F_5 Host_6 F_6 N_3 N_4 Edge Switch (Switch_B) F_B1 NPIV enabled F_B2 NPIV enabled Host_7 F_7 Host_8 F_8 FIGURE 3 Example F_Port-to-N_Port mapping Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 5 53-1001189-01