Adobe 22012057DM User Guide - Page 20
Adobe 22012057DM - Soundbooth CS3 - PC Manual
 |
UPC - 883919114866
View all Adobe 22012057DM manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
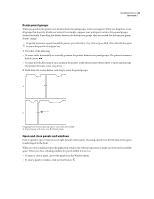
SOUNDBOOTH CS3 16 User Guide When you play a file in Soundbooth, the process happens in reverse. Soundbooth sends a series of digital samples to the sound card. The card reconstructs the original waveform and sends it as an analog signal through Line Out ports to your speakers. To sum up, the process of digitizing audio starts with a pressure wave in the air. A microphone converts this pressure wave into voltage changes. A sound card converts these voltage changes into digital samples. After analog sound becomes digital audio, Soundbooth can record, edit, and process it-the possibilities are limited only by your imagination.

SOUNDBOOTH CS3
User Guide
16
When you play a file in Soundbooth, the process happens in reverse. Soundbooth sends a series of digital samples to
the sound card. The card reconstructs the original waveform and sends it as an analog signal through Line Out ports
to your speakers.
To sum up, the process of digitizing audio starts with a pressure wave in the air. A microphone converts this pressure
wave into voltage changes. A sound card converts these voltage changes into digital samples. After analog sound
becomes digital audio, Soundbooth can record, edit, and process it—the possibilities are limited only by your imagi-
nation.