Cisco 7931G Administration Guide - Page 60
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
 |
UPC - 882658128578
View all Cisco 7931G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
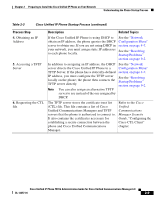
Understanding the Phone Startup Process Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco Unified IP Phone on Your Network For more information about how the phone interacts with the TFTP server, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager System Guide, "Cisco TFTP" chapter. Understanding the Phone Startup Process When connecting to the VoIP network, the Cisco Unified IP Phone goes through a standard startup process, as described in Table 2-3. Depending on your network configuration, not all of these process steps may occur on your Cisco Unified IP Phone. Table 2-3 Cisco Unified IP Phone Startup Process Process Step 1. Obtaining Power from the Switch 2. Loading the Stored Phone Image 3. Configuring VLAN Description Related Topics If a phone is not using external power, the switch See the "Providing provides in-line power through the Ethernet cable Power to the Phone" attached to the phone. section on page 2-4. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. The Cisco Unified IP Phone has non-volatile Flash memory in which it stores firmware images and user-defined preferences. At startup, the phone runs a bootstrap loader that loads a phone image stored in Flash memory. Using this image, the phone initializes its software and hardware. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. If the Cisco Unified IP Phone is connected to a Cisco switch, the switch next informs the phone of the voice VLAN defined on the switch port. The phone needs to know its VLAN membership before it can proceed with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request for an IP address. See the "Network Configuration Menu" section on page 4-7. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.0 2-8 OL-12457-01