Edimax EW-7238RPD Manual - Page 83
III-4-3. Administration Utility., II-5. Choosing the Best Location, for Your Wi-Fi Extender.
 |
View all Edimax EW-7238RPD manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
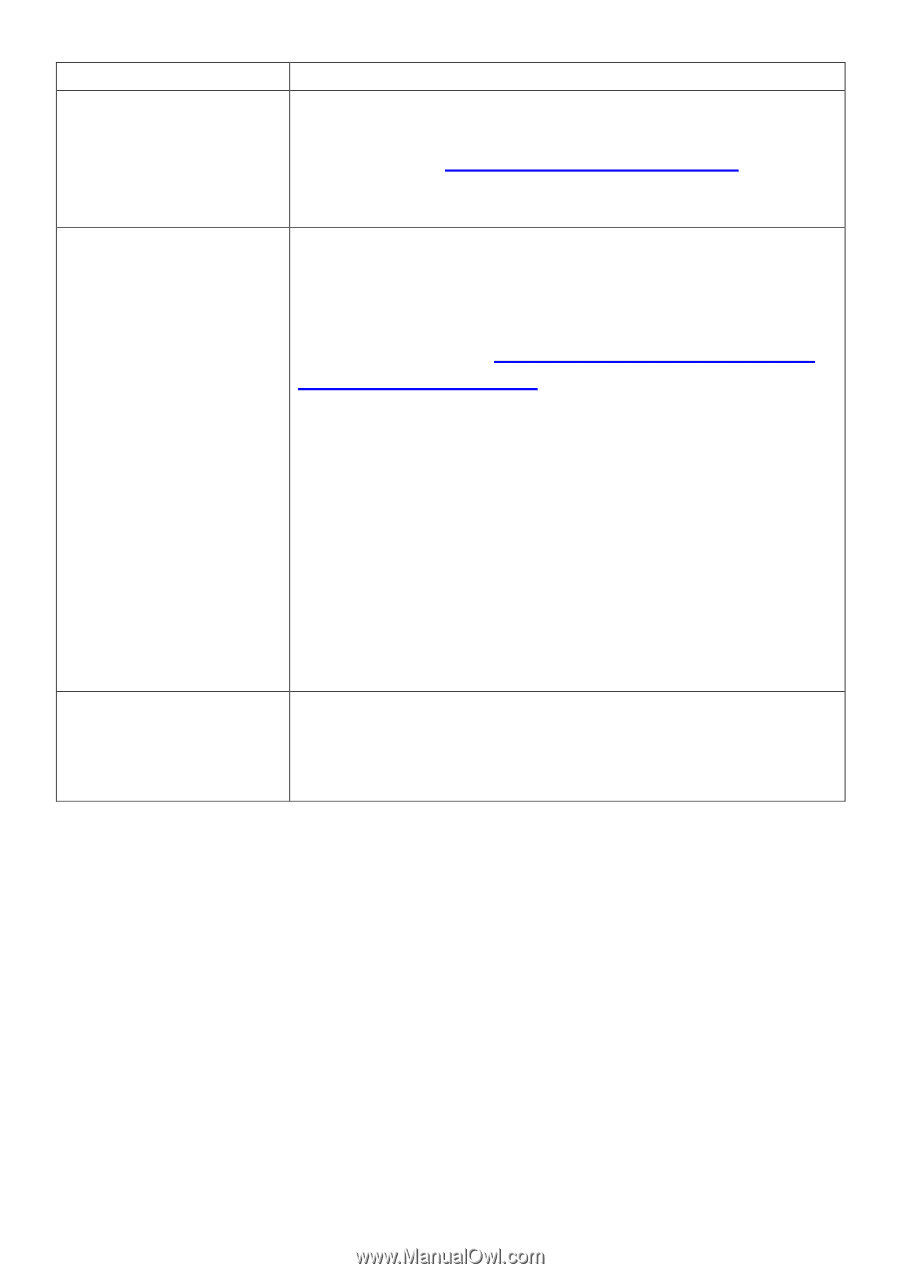
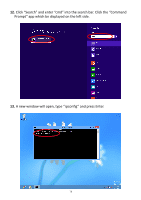
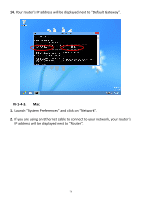
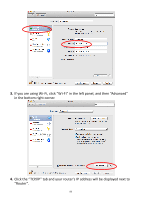
connected to your router/access point. My network is using a You can modify the IP address of the wireless bridge static IP address, how using the browser based configuration interface. do I assign an IP Please refer to III-4-3. Administration Utility. address to my wireless extender? My wireless extender The best location to place the Wi-Fi extender is one has a poor signal which is an open space, roughly in the middle from my access between your router and the Wi-Fi dead zone, and point/router. where the Wi-Fi extender LED displays "Excellent" signal strength. See II-5. Choosing the Best Location for Your Wi-Fi Extender. Can I use the same SSID as my current gateway router for my Wi-Fi extender? a. Keep the extender away from other radio devices such as microwaves or wireless telephones. b. Do not put the extender in the corner of a room or under/nearby metal. c. It is recommended to plug the extender directly into a wall socket. If it is necessary to use a multiple socket adapter then avoid placing the adapter on the floor. d. Ensure there are as few obstacles as possible between the extender and the access point/router. Yes, but it is not recommended as it will be difficult to distinguish between two SSIDs with the same name. IV-3. Glossary Default Gateway (Wireless bridge): Every non-access point IP device needs to configure a default gateway's IP address. When the device sends out an IP packet, if the destination is not on the same network, the device has to send the packet to its default gateway, which will then send it out towards the destination. DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol automatically gives every computer on your home network an IP address. DNS Server IP Address: DNS stands for Domain Name System, which allows Internet servers to have a domain name (such as www.Broadbandaccess 83