HP Indigo WS6000 Indigo High Quality Color Control HQCC Process for PSPs and B - Page 22
Substrate definition (PSP
 |
View all HP Indigo WS6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
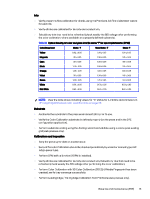
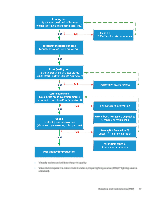
Final Calibration (pre-profiling) ○ Verify the implementation of the "recommended frequency of Color Calibration" table. ○ Perform Advanced Color Calibration with 3D calibration - V-electrode calibration - w/o start with default parameter, and Media Fingerprint - Verify it converged successfully, and that print quality is acceptable according to your end-user final expectations. ► Once the above process is completed, it is recommended to follow up immediately with any color profiling and spot color refinement that needs to be performed, or any color critical job that needs to be printed. - Calibrate the press for best color consistency following the steps below. Calibrating for best color consistency ○ Perform Advanced Color Calibration with 3D calibration - V-electrode calibration - w/o start with default parameter, and Media Fingerprint - Verify it converged successfully, and that print quality is acceptable according to your end-user final expectations. ● After replacing for new supplies ● After ink rebuild ● After BID replacement ● Before reprinting jobs ● Before any color-critical job ● After replacing the type of substrate ● After changing the type of Job LUT and / or screen type ● During long-run printing ○ Activate the Continuous Color Calibration (CCC). ○ Inspect the print quality and the solids OD of the press on a regular daily basis, depending on the printed application and the production workflow. ● Perform backup of the Press and DFE software parameters and configuration. Substrate definition (PSP) Correctly define the substrates. ● Define correctly all printed substrates. Substrate type PP White 50 µ PP White 50 µ PP Clear 50 µ PP Clear 50 µ Ink configuration CMYK OV CMYK OV CMYK OV CMYK OV Facestock definition Gloss Matt Gloss Matt 18 Chapter 3 Detailed production processes