HP Mellanox SX1018 Mellanox MLNX-OS User Manual for SX1018HP Ethernet Managed - Page 26
Syntax Conventions, Getting Help
 |
View all HP Mellanox SX1018 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
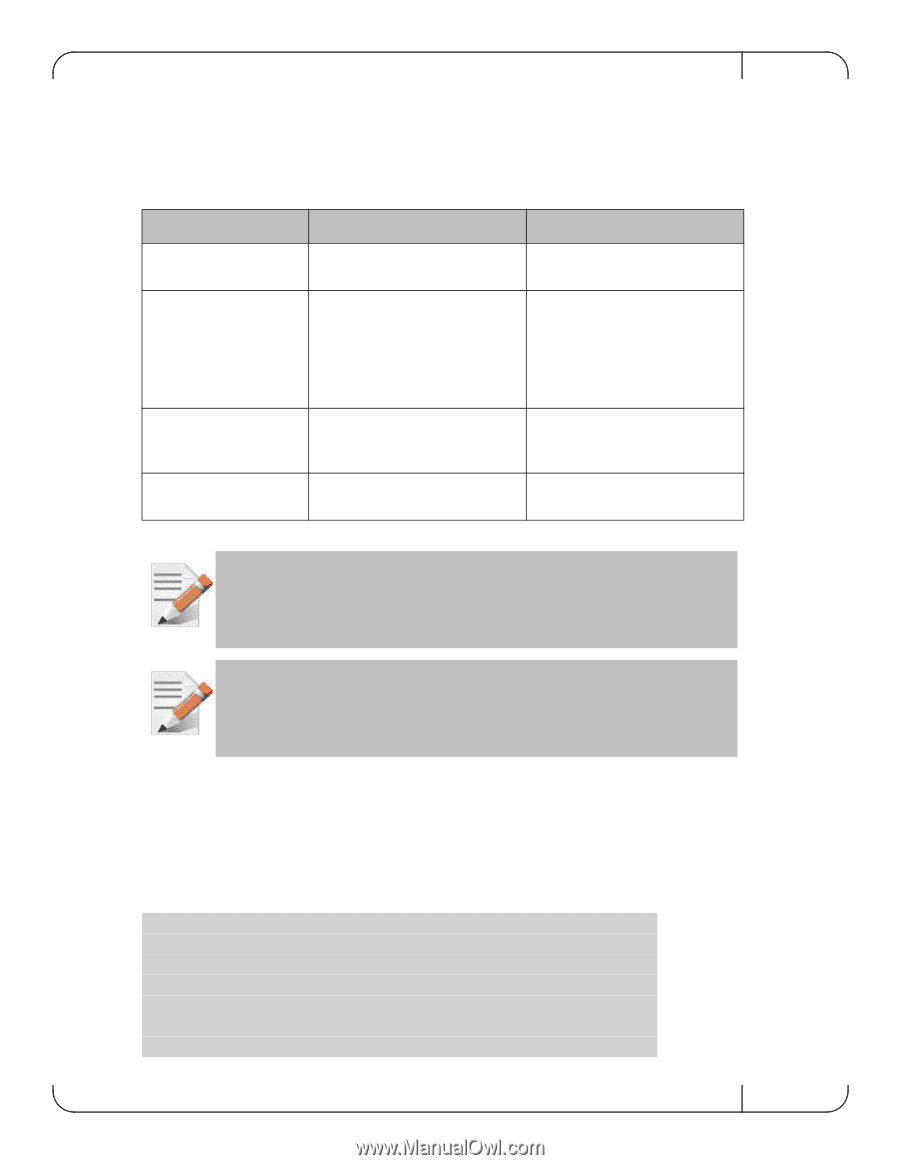
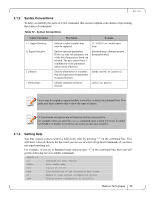
Rev 1.6.2 3.1.2 Syntax Conventions To help you identify the parts of a CLI command, this section explains conventions of presenting the syntax of commands. Table 12 - Syntax Conventions Syntax Convention < > Angled brackets [ ] Square brackets { } Braces | Vertical bars Description Example Indicate a value/variable that must be replaced. or Enclose optional parameters. However, only one parameter out of the list of parameters listed can be used. The user cannot have a combination of the parameters unless stated otherwise. [destination-ip | destination-port | destination-mac] Enclose alternatives or variables that are required for the parameter in square brackets. [mode {active | on | passive}] Identify mutually exclusive choices. active | on | passive Do not type the angled or square brackets, vertical bar, or braces in command lines. This guide uses these symbols only to show the types of entries. CLI commands and options are in lowercase and are case-sensitive. For example, when you enter the enable command, enter it all in lowercase. It cannot be ENABLE or Enable. Text entries you create are also case-sensitive. 3.1.3 Getting Help You may request context-sensitive help at any time by pressing "?" on the command line. This will show a list of choices for the word you are on, or a list of top-level commands if you have not typed anything yet. For example, if you are in Standard mode and you type "?" at the command line, then you will get the following list of available commands. switch > ? cli enable exit help no show Configure CLI shell options Enter enable mode Log out of the CLI View description of the interactive help system Negate or clear certain configuration options Display system configuration or statistics Mellanox Technologies 26