HP T5540 Administrator's Guide: Windows CE 6.0 - HP Thin Client t5530 and t554 - Page 58
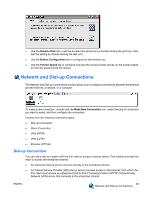
Direct Connection, Virtual Private Network (PPTP) Connection, PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE) Connection
 |
UPC - 884420407706
View all HP T5540 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 58 highlights
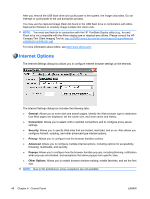
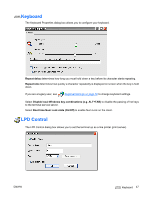
NOTE: The dial-up server must be a Microsoft Remote Access Server or another server that supports industry-standard protocols. Direct Connection This type of connection allows you to connect directly to another computer through the serial port on the terminal. NOTE: This option is available only to thin clients with serial ports. Virtual Private Network (PPTP) Connection Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables the secure transfer of data between a remote client (in this case the thin client) and an enterprise server environment by creating a VPN across TCP/IP-based data networks such as the Internet. It provides a password-protected path through the enterprise firewall to the enterprise server environment in which the network and session services required by the thin client reside. Access to the internet requires an Internet Service Provider (ISP). You may use any of the standard means of connecting to the ISP, such as a dial-up modem, cable modem, or DSL modem. You must first establish the connection to the ISP, before contacting the enterprise PPTP VPN server. This includes dial-up access as well as direct access through the cable modem and DSL modem paths. Virtual Private Network (L2TP) Connection Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) merges the Microsoft PPTP protocol with the Cisco Layer Two Forwarding (L2F) protocol. L2TP is basically the same as PPTP; the primary difference is that L2TP supports encryption. PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE) Connection This is a connection from the thin client Ethernet port directly to the enterprise intranet. No additional hardware is required. In this configuration all network services may be used, including the enterprise DHCP server. A DHCP server on the network may provide not only the terminal's IP address, but also the location of the file server containing the software updates. Port Lock The Port Lock dialog box allows you to enable or disable COM 1 ports, LPT ports, and USB mass storage devices. 50 Chapter 4 Control Panel ENWW